Summary Every year, many businesses lose billions because of cyberattacks. If you don’t want to become one of them, you must pay attention to IT security. Read on to learn what is IT security and why it matters for your business.
Think about how horrifying it must have been for the executives at Equifax to wake up to the news that their IT security failures had compromised the data of 143 million customers—more than 40% of the U.S. population! Congressional hearings followed, fines were levied, and careers were ruined, all because one of the U.S.’s three credit bureaus failed to provide a security patch on an application.
According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Report, businesses around the world experienced $4.2 billion in losses last year due to IT security holes, and that number is on the rise (showing a 200% increase over the previous three years).
The stark truth is that failing to protect your customers’ data and your trade secrets could destroy your business and open you to litigation. That’s why IT security is a must for organizations of any size.
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation, and a few minutes of cyber-incident to ruin it.” —Stéphane Nappo, Chief Information Security Officer for SEB
What is IT Security?
IT Security is the protection of computer networks and systems from data exposure, theft, or damage caused by nefarious agents—sometimes called “black hat” hackers. These bad actors use a variety of tools and techniques, from malware to brute force hacking, to bypass security systems and steal vital data from organizations and their customers. IT security is a vast field designed to protect against these threats.
Four Major Types of IT Security
Hackers will use any means available to break into your system, and each pathway to secure data represents a potential vulnerability. As such, specialists focus on different branches of IT security. Four of those major branches include internet security, cloud security, application security, and security tailored to the Internet of Things (IoT).
1. Internet Security
Internet security involves protecting information transmitted through browsers and other web-based applications. Protection measures include applications that recognize unusual traffic and spot malware. It also involves the use of anti-spyware/malware software, firewalls, and similar tools.
2. Cloud Security
A great deal of information lives on the cloud these days, leaving entire platforms and vital data exposed to bad actors. Cloud security is of particular importance to Software as a Service (SaaS) providers, who rely on open access to their platforms in their business model. Tools that protect against cloud security threats include:
3. Application Security
Application security involves developing software as secure as possible during the software development process, evaluating and protecting the code against security threats.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) Security
From smart factories to biometric security scanners, the Internet of Things (IoT) has become an integral part of how we do business and navigate our everyday lives. When those systems are vulnerable to IT security threats, hackers can wreak all sorts of havoc and cost companies billions of dollars.
IoT Security involves creating security hardware and operating systems, using the same kind of end-point security that experts use to keep your smartphones, tablets, and other devices as safe and secure as possible.
Why IT Security is Essential for Your Businesses
Powerful IT security is vital for any business, whether you run a multinational firm that handles top-secret government contracts or a small SaaS startup that’s looking to become the next unicorn.
No matter what your business does, if you handle sensitive customer data or hope to maintain your business secrets, you have a duty to your customers and your investors to keep that data secure. Healthcare data security for example is a glaring example of spheres that call for alertness and precaution – you cannot afford to risk the medical records of patients at any cost.
The following reasons are crucial when it comes to deciding about IT security.
1. Confidentiality Requirements
You are legally and ethically bound to keep your customers’ data secure—from their credit card information to their activities within your platform. This not only means protecting stored data, it also involves securing data through state-of-the-art encryption techniques.
2. Ensuring Information Integrity
Hackers aren’t only out to steal your data. Many will try to manipulate your data for a variety of reasons. Your website security can only survive if you can trust your data. IT security seeks to ensure information integrity, so you can have confidence in the data your system relies on.
3. Maintaining Information Availability
Data breaches can wreak havoc on a system, whether the bad actors are out to steal data, manipulate it, or hold it hostage. In fact, some hackers set out to do nothing more than incite chaos within your platform! Rather than attempting to steal or manipulate your data, these digital vandals may just be out to sabotage your business. After all, when you can’t access the right information at the right time, your business could fall apart.
Proper IT security protects against any activity that separates authorized personnel in your organization from the data they need to keep your business afloat.
4. Protecting Against Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) is an umbrella term that describes a variety of attacks that hackers use to disrupt your business and render you unable to serve your customers. The most common example of a dirty DoS trick is an overflow buffer attack, which involves sending a massive influx of traffic to your server which is far more than your engineers anticipated and beyond what your platform can handle.
IT security protects against this type of attack by flagging unusual traffic and stopping it in its tracks before it can overwhelm your system and harm your business.
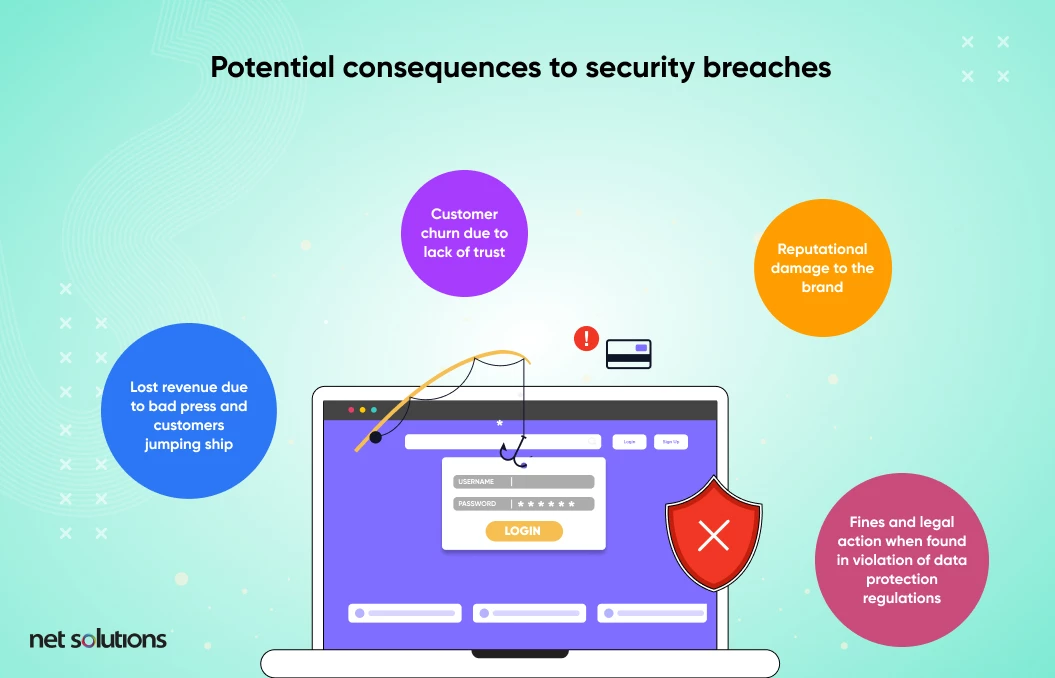
Business and Financial Implications of IT Security Breaches
IT security breaches are no joke, and the impact can be severe—from lost profits to legal consequences (in the case of negligence). You may recall reading about Yahoo!, Boeing, Facebook, and (of course) Equifax. Each of these organizations has dealt with IT security breaches and suffered various consequences.
Some potential consequences to IT security breaches include:
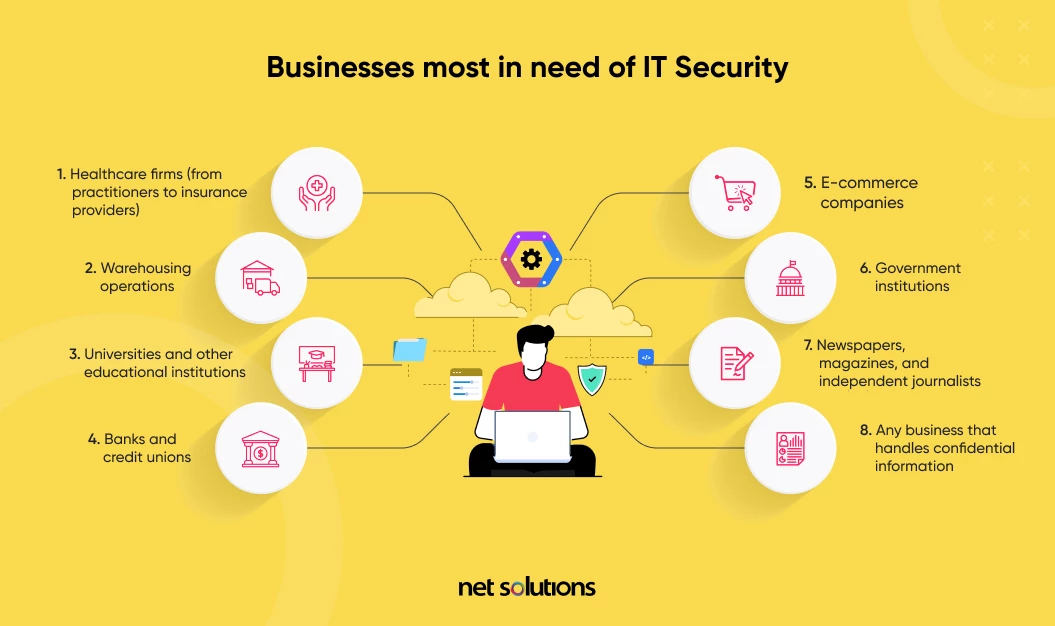
Businesses Most in Need of IT Security
Any business that handles sensitive customer data in any form should take IT security very seriously. That said, there are certain industries that are legally and ethically bound to operate at the top of their IT security game due to the heightened sensitivity of their data.
These companies include:
- Healthcare firms (from practitioners to insurance providers)
- Warehousing operations
- Universities and other educational institutions
- Banks and credit unions
- E-commerce companies
- Government institutions
- Newspapers, magazines, and independent journalists
- Any business that handles confidential information
Know Your IT Security Threats
There are some common threats to IT security, and it’s important to know what IT security efforts are generally designed to protect against. The following list is by no means exhaustive, but it’s a good summary of the usual suspects.
1. Malware
Malware describes any type of malicious software designed to interfere with your platform, network, server, or system. Malware can siphon private data, obtain access to the inner workings of your system, and perform all sorts of unsavory tasks. Malware often enters your system through human error, after employees click on a link they shouldn’t have clicked on (often presented to them in a phishing email, which you can read about below).
2. Adware
Adware is a type of malware that works its way into a system and often generates advertisements that appear in a browser when a user accesses the internet.
3. Ransomware
Ransomware is a particularly sinister kind of malware that invades a system and typically blocks access to the data unless the victim pays a ransom.
4. Spyware
Spyware is a type of malware that collects sensitive data of individual users or organizations, then delivers that data to bad actors who can do all sorts of terrible things with it.
5. Computer Viruses
The term “computer viruses,” like malware, describes a broad category of software used for illicit purposes. Often the bad guys use viruses to simply unleash chaos on the world. Picture a supervillain who doesn’t get out much.
6. Phishing
Phishing is a technique used to trick users into either clicking on a link that downloads malware or convinces users to give up sensitive information. Phishing attempts have become extremely sophisticated, often spoofing legitimate domains from banks and other trusted institutions.
7. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack
Early we talked about Denial of Service attacks, where a large number of bots bombard a website or platform with traffic, overwhelming it and rendering it inoperable. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a DoS attack that comes from a wider range of traffic sources, distributed across the globe, making it even more difficult to stop.
8. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are hacking attempts that gain access to a network or platform and remain undetected for long periods of time. These are often state-sponsored security threats, such as the Russian government’s hacking of the U.S. Democratic National Committee and Hillary Clinton’s 2016 presidential campaign.
9. Botnets
Botnets consist of numerous distributed devices connected to the internet. These bots can engage in Distributed Denial-of-Service attacks and other nefarious activities, such as data theft and spam distribution from your company’s email addresses.
How to Boost Your IT Security
What can you do to reduce your risk of becoming the next victim of an IT security breach? Working with a professional IT security firm or hiring internal IT security staff is a good first step
Security as a Service (SECaaS) is a business model where security companies provide tailored, ongoing IT security support to organizations that need it. These professionals will likely have you perform the following steps:
- Perform a threat audit that evaluates your current IT security setup and models potential threats that might impact your business
- Educate employees to make them aware of the various threats, internalize best practices, and remain on the lookout for phishing attempts, malware threats, and other dangers
- Implement Security by Design, an approach to testing software vulnerability throughout the development process. Security by Design consultants can guide you in your efforts, using so-called “white hat” hackers to find security holes in your products
- Use a suite of security appliances, which includes any tools used to deliver IT security: firewalls, encryption, content filtering, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an IT security breach and how does it happen?
An IT security breach occurs when an unauthorized entity (a hacker or a bot deployed by hackers) gains access to sensitive data on your network, platform, or website. Hackers can gain access through a variety of means, including manual phishing attempts and the automatic distribution of malware.
2. Why is IT security important?
Failure to secure your company’s IT systems can result in:
- Financial loss due to loss of market share, since customers no longer trust your brand
- Reputation loss that occurs the instant news breaks about your security breach
- Operational downtime that is caused by the many hours your IT staff will spend fixing issues
3. What does it mean when a website is not secured?
When you receive a warning that a website is “not secure,” your browser is telling you that the website has not installed an SSL certificate. When a webmaster uses an SSL certificate, that means the website’s URL uses the secure “HTTPS” protocol instead of the insecure “HTTP.” Without getting too technical, the HTTPS that appears in front of a website’s URL indicates a secure connection, so the website can more safely transfer sensitive data (such as payment information).
Keep Your Business & Customers Safe from Cyberthreats
Talk to our experts to build security into your IT infrastructure.


 Updated: May 9, 2022
Updated: May 9, 2022