Business-to-business (B2B) sales continue to shift online, with B2B eCommerce representing over $2.4 trillion in annual sales. As B2B businesses evolve their selling practices, eCommerce is no longer a ‘nice to have’, but a ‘must have’ capability. In fact, with consumer preferences influencing the B2B space, the demand for sophisticated, personalized eCommerce capabilities continues to grow.
This guide will walk you through:
- A clear definition of B2B eCommerce and how it differs from B2C (business-to-consumer)
- Why now is more critical than ever to invest in B2B eCommerce
- Some of the top B2B eCommerce platforms and features you should know about
- Key trends and advancements in B2B eCommerce
- How to get started with or advance your B2B eCommerce strategy
This guide will represent industry best practices as well as insights gained from working directly with B2B clients to design, build and grow B2B stores. Learn more about Net Solutions and our eCommerce Development Services or reach out to get started.
What is B2B eCommerce?
B2B eCommerce is the buying and selling process between two businesses. In business-to-business (B2B) eCommerce, a B2B seller will market and sell a product, service or software to another via an online sales platform.
B2B eCommerce is often supported by a B2B eCommerce platform that includes unique features and workflows necessary to support B2B buyers and sellers.
B2B eCommerce sales grew 17% in 2023, with no sign of slowing down. In fact, 90% of all B2B businesses now support eCommerce, with 80% holding their eCommerce channel to a higher than ‘basic’ standard. Today, more than one third of B2B buyers would make online purchases of $500k or more, and 15% would easily purchase over $1 million.What is the Difference Between B2B and B2C eCommerce?
The main difference between B2B and B2C eCommerce is the buyer: either consumer or business.
B2C stands for business-to-consumer eCommerce. As the name implies, in a B2C business setup, the business is the seller, and the end-user, or the consumer, is the buyer. There are no intermediary parties in between. On the other hand, in a B2B business setup, the buyer and the seller are both business entities. The buyer may act as an intermediary, who can then sell the products/services to the end-users.
The key differences between B2B and B2C eCommerce are listed in the following table:
| B2B eCommerce | B2C eCommerce | |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Makers | Multiple | Single (majorly millennials) |
| Purchase Type |
|
|
| Buying journey |
|
|
| CTAs (Call-to-Action) | Revolves around how the product/service benefits the customer’s business | Revolves around how the product/service benefits the customer |
| Website Design |
|
|
| Level of Customer Support |
|
|
| Checkout Process |
|
|
| Catalog and Pricing Model |
|
|
This guide will further detail the differences associated with B2B eCommerce.
What are the Different Types of B2B eCommerce Businesses?
The different types of B2B eCommerce businesses are listed below:
1. B2B2B
B2B2B stands for “business to business to business” — an eCommerce model that adds additional parties in the B2B chain. These intermediaries or partnerships could be distributors, sub-distributors, resellers, brokers or wholesalers.
ExampleIn B2B2B, a manufacturer may sell a product via a reseller who then would sell it to the end customer (a business). Another example could be software companies who leverage third-party distributor partners or system integrators to sell their products to the end customer (still a business). These intermediaries play a role in marketing and selling the products or services.
2. B2B2C
B2B2C stands for “business to business to consumer” — an eCommerce model that also involves a business and an intermediary to sell goods or services to end customers. In this model, the end customer is a consumer (not a business), bridging the gap between B2B and B2C businesses.
ExampleAn example of B2B2C includes grocery stores delivering groceries to end-consumers with a third-party such as Instacart or marketplaces such as Amazon or digital app stores that allow online retailers a chance to market and sell their goods to end consumers. B2B2C models have grown significantly based on shopping habits, with 60% of B2B buyers saying they are open to purchasing on digital marketplaces.
3. Wholesalers
In a wholesale setup, a business buys bulk products from the manufacturer or a distributor at a much lower price to then sell at a retail price to other businesses (often retailers), although some wholesalers sell direct to consumers (e.g. Costco). While a retailer can buy directly from a manufacturer, a wholesaler may offer greater stock flexibility if they purchase from multiple manufacturers.
Wholesalers are an intermediary in B2B2C or B2B2B models, which is often referred to as “B2B2X” to denote the variability in the end customer.4. Manufacturers
Manufacturers are producers of the products that run large-scale productions at their end. Manufacturers are the first “B” in any product-based B2B network, but the model could be:
- B2B – The manufacturer sells direct to another business using an eCommerce channel
- B2B2x – The manufacturer leverages an intermediary (distributor, reseller, wholesaler, supplier etc) to sell to the end customer.
5. Distributors
A distributor is an intermediary who assumes responsibility in marketing or selling a manufacturer or producer’s product to retailers or to the end customer, managing all the logistics of fulfillment. Distributors often deal in a lower volume of products than wholesalers.
An example of this is a local car part store that purchases a variety of car parts and resells them to local mechanic shops.6. Service or Software-Based B2B
B2B companies may also supply services (e.g. accounting services) or software (physical or software-as-a-service) to other businesses. As with other B2B businesses, intermediaries can be involved to market and sell services to the end customers (B2B2X).
Chapter 1 B2B eCommerce Benefits
The global B2B eCommerce market is set to grow to $36.1 trillion by 2026, with an estimate of 80% of all B2B sales interactions moving to digital channels by 2025. This is a significant shift, one that isn’t prompted by fear, but instead from the direct benefits of a strong eCommerce strategy, which include:
- Greater scalability and growth of the business by having a wider reach to more customers across new channels and regions
- Reduced marketing costs to reach customers where they are more efficiently, through new channels or via intermediaries
- Increased order value for customer by making purchasing more convenient (self-service, reorders, volume discounts)
- Streamlined operations, with the eCommerce software taking orders any time of day, creating packing slips, invoicing, and tracking fulfillment
Chapter 2 B2B eCommerce Platforms
At the heart of the B2B eCommerce business is a B2B eCommerce platform, a software solution designed to support the buying and selling between two businesses. This B2B eCommerce platform has either been specifically designed to support the needs of B2B buyers and sellers or is an add-on / extension to a B2C platform, adding essential features to support B2B eCommerce.
Examples of B2B eCommerce platforms include:- BigCommerce – A headless platform for B2B, B2C and multi-storefront selling
- Adobe Commerce – An enterprise platform for B2B, B2C and marketplaces
- commercetools – a composable commerce platform for complex B2B, B2C and marketplace businesses
Chapter 3 Cost of B2B eCommerce Platforms
There is a great deal of variability in the cost of B2B eCommerce platforms. First and foremost, the cost depends on whether the platform is open-source (self-hosted) or licensed (for self-hosting or cloud offering). Other factors that influence the B2B eCommerce platform cost cost include:
- Hosting costs (depending on open-source vs SaaS or PaaS)
- Third-party add-ons or extensions (one-time or subscription fees)
- Website design & development costs (up-front and ongoing)
- Payment processing fees for B2B transactions
- Ongoing maintenance and support
Chapter 4 B2B eCommerce Features
The choice in B2B eCommerce platform can have a significant impact on business outcomes, including efficiency, growth, and the customer experience. When comparing platforms, B2B businesses should consider the following features:
- Self-service portal for buyers to manage shopping lists, view invoices, purchase orders and tracking information, and easily re-purchase
- Corporate account management, with access controls, roles & permissions and the ability for sales to complete a purchase
- Differentiated catalogs and pricing models (more on this later in this guide)
- Bulk ordering, to support distributors and wholesalers or large business customers
- Alternate payment methods, including ACH, wire transfer, check, credit card and virtual card
Chapter 5 B2B eCommerce Challenges
Today’s B2B buyer comes to the purchase experience with all new expectations and very little patience if these expectations are not met. In fact, 90% of buyers would switch to a competitor if they offered a better online customer experience. Some of the biggest challenges today’s B2B eCommerce sellers face are:
- The need to deliver a personalized buying experience, from pricing and promotions to catalogs and search
- The need to support buying processes that have many stakeholders (an average of 6-8)
- Evolving shipping requirements and preferences, including shifting preferences on order size, a desire for sustainable shipping practices, or a preference for transparent shipping costs and timelines
Thankfully, as we will demonstrate in our post on B2B eCommerce challenges, for each challenge there is a solution to be had with the right platform, tools, and strategy.
Chapter 6 B2B eCommerce Catalog
B2B companies often struggle with managing complex product data across channels and systems or in presenting large, technical or customizable products in a way that’s easy to understand. Enter: catalog management. Today’s B2B eCommerce platforms are helping take the pain out of digital catalog management by:
- Integrating seamlessly with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and inventory management solutions
- Leveraging dynamic filters and advanced search (including new AI capabilities) to offer personalization of the entire catalog and during search and browsing
- Leveraging mobile-first design principles to ensure catalogs support all stages of the buying journey, which more often than not include mobile
Chapter 7 B2B eCommerce Website Examples
With all the shifting trends and preferences and B2B eCommerce platforms transforming at a rapid clip, with new features and evolving technologies (we’ll get to some of these later), it can be hard to know what a ‘good’ B2B website looks like anymore.
Take, for example, Alibaba: one of the world’s top B2B players. Using Alibaba.com, manufacturers can sell to retailers around the world, helping increase the global reach for these products. With such a global audience, Alibaba has ensured that it supports an extensive number of payment options, including those regional to certain geographic areas (such as Boleto in Brazil). Alibaba has also created a messaging center to help retailers and sellers speak one-on-one, available on the web or using a mobile app.
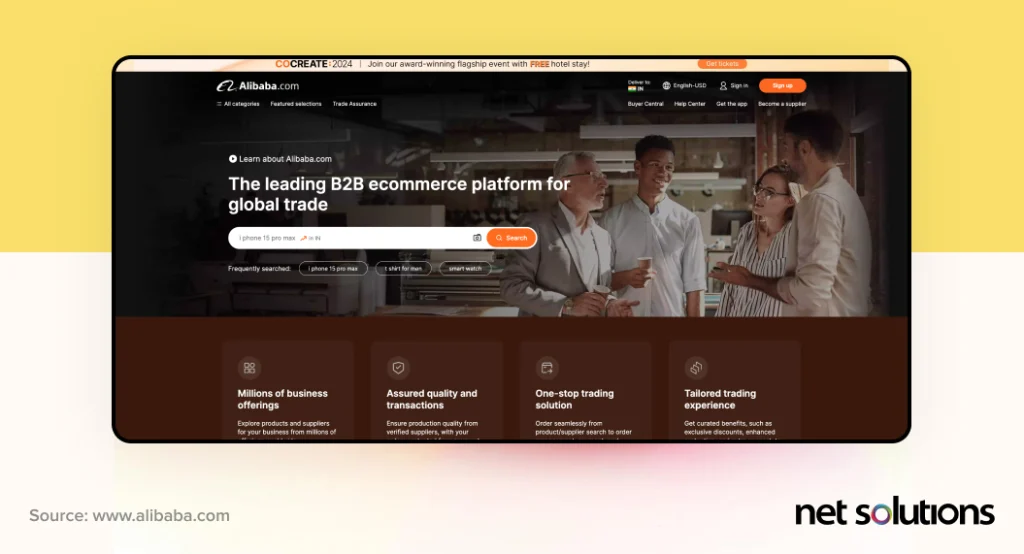
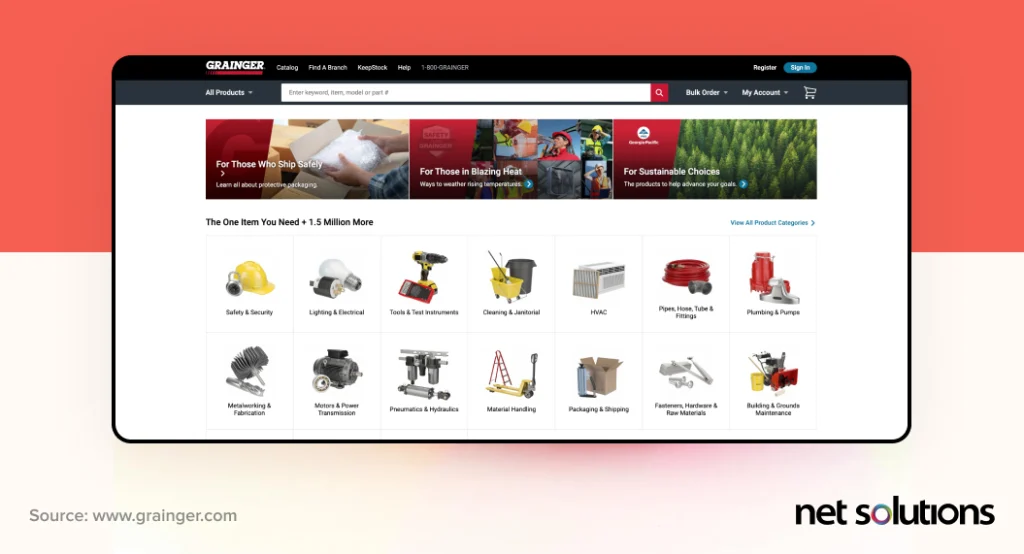
We also love what Grainger is doing. Grainger is a leading distributor of industrial supplies and equipment, supporting a whopping 1 million products. How does Grainger navigate this complexity? With clear, photo-based categorization, smart filtering, and advanced search capabilities. Further, Grainger supports side-by-side comparisons of products, making it easier for buyers to do their purchasing.
We’ve compiled a list of what we think are the 9 Best B2B eCommerce Websites in 2024. We hope you’re inspired!
Chapter 8 B2B eCommerce Trends
We’ve made a few allusions, but this guide would not be complete without providing a more comprehensive picture of some of the latest B2B eCommerce trends, including:
- How buyers are interacting with more channels than ever before (10 channels, in fact), driving the demand for headless commerce: an eCommerce platform architecture that optimizes performance and experience across channels (more on this later).
- How genAI is impacting B2B in a wide variety of ways, from workflow automation and search to website personalization
- A growing demand for faster order fulfillment (even amidst today’s supply chain woes).
It can be hard to know which trends are important and which are passing fads. We’ve worked to put together what we consider the most critical B2B eCommerce trends of 2024.
Facing the future, consider the importance of partnering with an experienced eCommerce development company who works with many clients across B2B to help you decide which trends are worth paying attention to.
Chapter 9 B2B eCommerce Website Development
B2B eCommerce website development encompasses all the work required to design and build an eCommerce site for B2B sales. This requires more than just a website, more than a standard eCommerce platform, and more care to the B2B buying journey both in development and design. Your website is ultimately influenced by:
- Business model / buyer / business goals
- The eCommerce platform you choose and the plethora of decisions therein (features, integrations)
- How you design the user experience (UX)
- What powers your back end operations (and how it relates to your eCommerce platform)
Of course, we would be doing you a disservice if we did not offer you a comprehensive guide to help assist your decision-making in B2B eCommerce Website Development.
Chapter 10 B2B Mobile eCommerce
B2B Mobile eCommerce includes creating a strategy that includes ensuring that all your digital channels are served well on a mobile device, which could mean quite a lot of things: having a mobile-friendly web design, building a mobile app, creating a strategy for social media, setting up self-serve portals for mobile navigation, creating a strategy for sales team enablement across channels, and so much more.
If you’re new to B2B mobile eCommerce, you want to know:
- What is B2B mobile eCommerce?
- What are the advantages to supporting mobile?
- How can your eCommerce platform help?
- What are the critical user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design elements to consider?
Chapter 11 B2B eCommerce Mobile Apps
A B2B eCommerce mobile app is a dedicated app (or potentially a progressive web app) that helps your users interact with your eCommerce store. A B2B mobile app may be designed to work on all mobile devices or may include different apps for each mobile device (e.g. iOS vs Android).
Mobile apps are known for:
- Increased performance on mobile devices
- Supporting the user experience with improved self-service capabilities
- Meeting accessibility goals
- Offering more interactive features such as in-app messaging and chat
Chapter 12 UX in B2B eCommerce
User experience (UX) represents the overall experience a buyer has when using a website and eCommerce store. A great user experience will help build trust in the early stages of a buying journey and keep your buyers coming back, making it easy to repeat purchases and become advocates for your brand.
Today, only 36% of B2B buyers would rate their purchase experiences as an “A,” so there’s definitely room for improvement. And that improvement has to be specific to the needs of the B2B buying journey, such as:
- Intuitive navigation, personalization, search and filtering capabilities to support large and complex catalogs
- Optimizing self-service portals and checkout experiences for different B2B buyer groups
- Incorporating multiple ways to capture leads
To start with, we’ll take you back to the basics of UX in B2B eCommerce.
UX design is as much a science as it is an art, often involving persona research, stakeholder interviews, content audits, buyer journey mapping, prototyping and thorough testing. If this exceeds your capacity or experience, we’d love to help.
Chapter 13 B2B eCommerce Pricing
In B2B, pricing models will differ from B2C (standard flat pricing), involving a variety of pricing models from per-client pricing to cost-plus pricing or subscription pricing. Knowing the pros and cons of each model can help you determine which B2B pricing model is right for you, as well as best practices including:
- The importance of matching pricing to the communicated value of your products
- Monitor competitors’ pricing
- Take into account a customer’s willingness to pay (and their tolerance for price change)
Chapter 14 Headless B2B eCommerce Platforms
A traditional B2B eCommerce platform is an all-in-one solution that makes it easy to create, launch and manage an online store, usually optimized for the web, and sometimes responsive to mobile. While simple to launch, as B2B demands increase across channels, poor performance in mobile or a lack of social channels can really hold a business back.
Headless commerce architecture refers to a “decoupling” or separation of the front-end and back-end systems of the architecture, making it possible to create separate front-end experiences across channels (mobile, social, wearables), optimizing the tech stack, and creating a more efficient, scalable, and agile B2B operation. Headless commerce is:
- Flexible, allowing developers to make changes to the front-end to adapt to evolving buyer needs without impacting the performance of the whole
- Higher performing, with content stored in one place and delivered to multiple optimized channel front-ends simultaneously
- Optimized for omnichannel sales, becoming a single pane of glass for sales across channels, managing inventory in real-time, keeping prices in sync, simplifying fulfillment, and gaining the benefit of centralized business intelligence
Headless content management systems (CMS), which power eCommerce, are revolutionizing how B2B businesses operate.
Chapter 15 Open Source B2B eCommerce Platforms
All of this can seem both overwhelming and cost prohibitive for small or startup B2B brands, or for brands that need to retain tight control over their data, but that doesn’t have to be the case. There are many B2B eCommerce open-source platforms available free of charge (though you need to set up, host and manage them), creating a more inexpensive and controlled path to opening your own online store.
Open-source platforms are:
- Free to download, use, and modify
- Require you to manage hosting, APIs, security, integrations (both to internal systems such as CRM and third-party services), and maintenance
- Highly customizable
Some of the most notable open-source B2B platforms are Magento Open Source (full-featured, deep developer skills to set up but intuitive to use) and WooCommerce (an add-on for WordPress, easy to use, but less full-featured for B2B).
Chapter 16 B2B eCommerce for Fashion Brands
In the world of fashion, B2B fashion eCommerce is one of the fastest growing sectors, with B2B companies selling in bulk to wholesalers and creating a whole new way for retailers to buy fashion, either direct from a manufacturer, from a single wholesaler or through B2B marketplaces. Some of the benefits of B2B fashion eCommerce are:
- Ability to scale to global markets
- Reduced operational costs for B2B purchases
- Advanced analytics about customer behavior and site metrics to inform marketing, optimize the buyer experience, and even inform product offerings.
Chapter 17 AI in B2B eCommerce
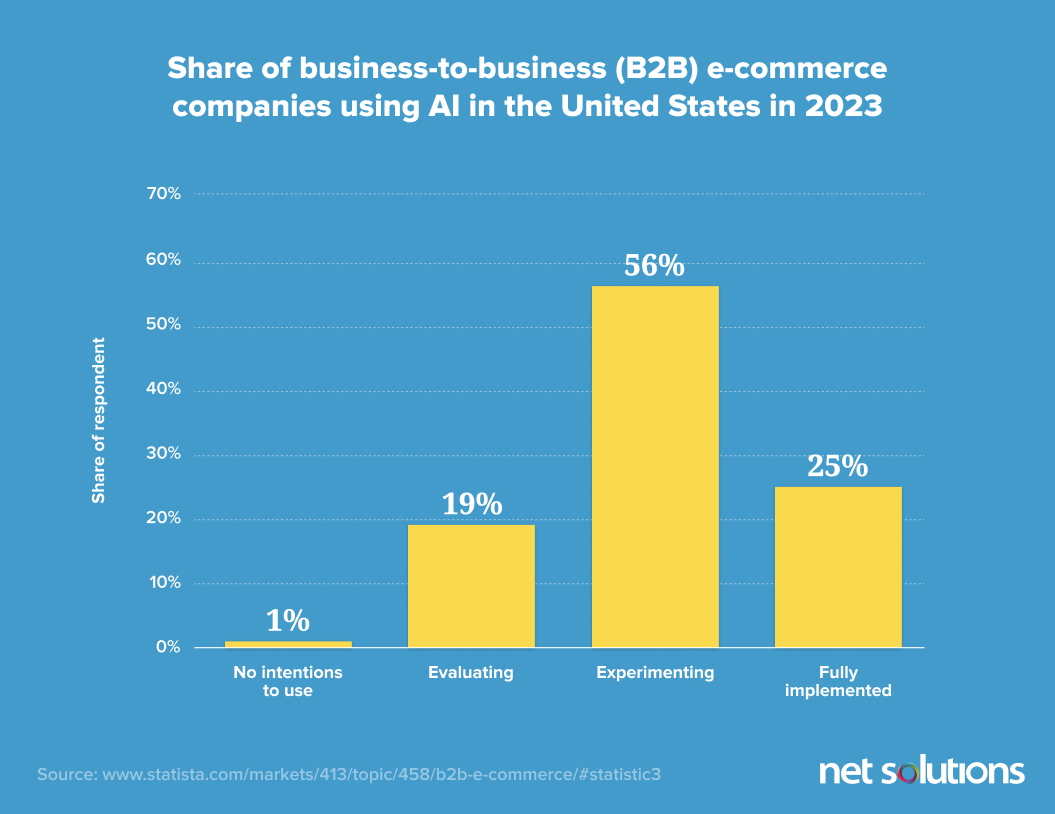
At least 56% of B2B businesses are experimenting with AI tools in the US, with AI being used on the back end to streamline operational workflows, generate and optimize product descriptions. On the front-end, AI is being integrated into chatbots, smarter search, product filtering and personalization (pricing, offers, product sorts).
There are many ways to begin with AI, including leveraging an advanced eCommerce platform with built-in capabilities to leveraging third-party integrations for specific AI capabilities.
Chapter 18 B2B eCommerce Metrics
To drive sales and growth across channels, you need to measure the success of your search engine optimization (SEO), your sales process, and your marketing efforts and to ensure that the B2B customers you spend money acquiring actually stick with you. With a vast amount of data available, it can be easy to get bogged down by information. Which metrics are important for your business? We’ve compiled a list of essential B2B eCommerce metrics we think every B2B business should track, including:
- Conversion rate
- Sales-qualified leads (SQLs)
- Customer lifetime value (CLV) to customer acquisition cost (CAC) ratio
- Cart abandonment rate
Chapter 19 B2B eCommerce Replatforming
At this stage, you may see that B2B eCommerce platforms offer a wide array of features and capabilities to help you operate a B2B business and manage sales and marketing. In fact, many of these capabilities can be built right into your platform – no third-party extension required.
However, if you’re looking at these chapters and thinking “my eCommerce platform can’t do any of this,” it’s time to replatform.
Maybe you started on an open-source platform such as Drupal and now you’d like to move to a cloud-hosted digital commerce platform like Adobe Commerce. Or maybe you’ve been using a traditional CMS such as WordPress and WooCommerce and you’d like to move to a headless CMS such as BigCommerce, Contentful or Sanity.
Replatforming is the process of migrating data from one eCommerce platform to another. While there is a cost to replatforming, the additional capabilities often directly impact those important metrics we just mentioned.
Need a High Functioning B2B eCommerce Website?
B2B eCommerce offers new and growing opportunities for B2B companies: to reach new markets, engage with new customers, meet customer needs, and offer a superior customer experience across sales channels. If you’re ready to take your B2B business to the next level and either start a project or replatform your eCommerce store, we’re here to help.
Net Solutions eCommerce development services can help you navigate which platform is right for your specific needs and help you design and develop a B2B eCommerce website that exceeds your business buyers’ expectations.
SHARE THIS POST
Table of Contents
Related Resources
- AI in B2B eCommerce: Everything You Need to Know
- Top 14 B2B eCommerce Benefits in 2024
- The B2B eCommerce Catalog: Everything You Need to Know
- The Biggest B2B eCommerce Challenges (And How to Address Them)
- The Ultimate Guide to B2B Fashion eCommerce: Strategies, Trends, and Solutions
- 18 Must-Have B2B eCommerce Features To Look For in 2024
- Headless B2B eCommerce - How to Redefine Your Business
- B2B eCommerce Marketplaces: Your In-Depth Guide
- Top B2B eCommerce Metrics to Track for Success [2024]
- B2B Mobile eCommerce - A Comprehensive Guide
- Why Your Business Needs a B2B eCommerce Mobile App
- 11 Top B2B eCommerce Open Source Platforms for 2024 [With Real Reviews]
- B2B eCommerce Platform Costs: A Comprehensive Guide (2024)
- 12 Top B2B eCommerce Platforms for 2024 [With Real Reviews]
- B2B eCommerce Pricing Strategies: An In-Depth Guide
- Your In-Depth Guide to B2B eCommerce Replatforming
- Top 9 B2B eCommerce Trends to Watch in 2024
- B2B eCommerce UX: A Comprehensive Guide
- A Step-by-step Guide to B2B eCommerce Website Development
- 9 of the Best B2B eCommerce Website Examples in 2024



