Delivering a seamless, customer-friendly eCommerce experience is no longer a differentiator. It’s a necessity for forward-thinking entrepreneurs to survive.
Amazon, eBay, and Walmart are examples of eCommerce websites.
We’ve created this guide to help you understand the nuances of eCommerce, the development solutions, and how to leverage them to build, launch, and establish your online store successfully.
What is eCommerce?
eCommerce involves building online platforms that facilitate the selling and buying goods and services over the Internet. These platforms bridge businesses to consumers and are digital storefronts where businesses can showcase their products/services, and customers can search, select, and buy them.
It includes activities such as auctions, payment gateways, online ticketing systems, and internet banking. eCommerce allows people to shop from anywhere at any time. It also provides a range of product options along with easy price comparisons. Furthermore, customers often enjoy reduced prices when shopping through eCommerce platforms.
eCommerce encompasses tools and platforms like email, online catalogs, shopping carts, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) File Transfer Protocol, and web services. Since its inception, eCommerce has greatly transformed how businesses function, and consumers purchase products.
Chapter 1Types of eCommerce Business Models
One of the first things to understand during eCommerce development is the different eCommerce business models and choose the one that’s right for your business. You can gain insight into the various eCommerce models in our blog post.
Here are the three most popular eCommerce business models delivering the shopping experiences consumers expect from retailers today:
1. Traditional B2B/B2C Model
In the traditional model, businesses provide products and services to other businesses (B2B eCommerce) or directly to consumers (B2C eCommerce). Examples of Traditional B2C Models are Amazon, Walmart, and Nike. Examples of Traditional B2B Models are Hubspot, Salesforce, and McKinsey.
- B2B2B or business to business to business, adds some additional parties to the model, like distributors, sub-distributors, wholesalers, etc.
- B2B2C or business to business to consumer, where B2B businesses can sell directly to customers or through partnerships with B2B businesses (e.g., Amazon Business).
- Direct-to-consumer(D2C), eCommerce is a strategy in which manufacturers or brands sell their products directly to customers without involving middlemen such as retailers or wholesalers.
- Wholesale, wherein businesses will buy products from manufacturers and could sell to other businesses, e.g., Alibaba.
- Manufacturers who decide to directly sell to customers or other businesses on an exclusive eCommerce platform besides being a part of the B2B network.
- Distributors who help manufacturers bring their products and services to the market. Sometimes, they set up their websites to take the lead.
Magento, Shopify, Salesforce Commerce Cloud, BigCommerce, Wix, and PrestaShop are some of the key platforms in this category. Choosing the best eCommerce platform lays the foundation for a robust B2B eCommerce business.
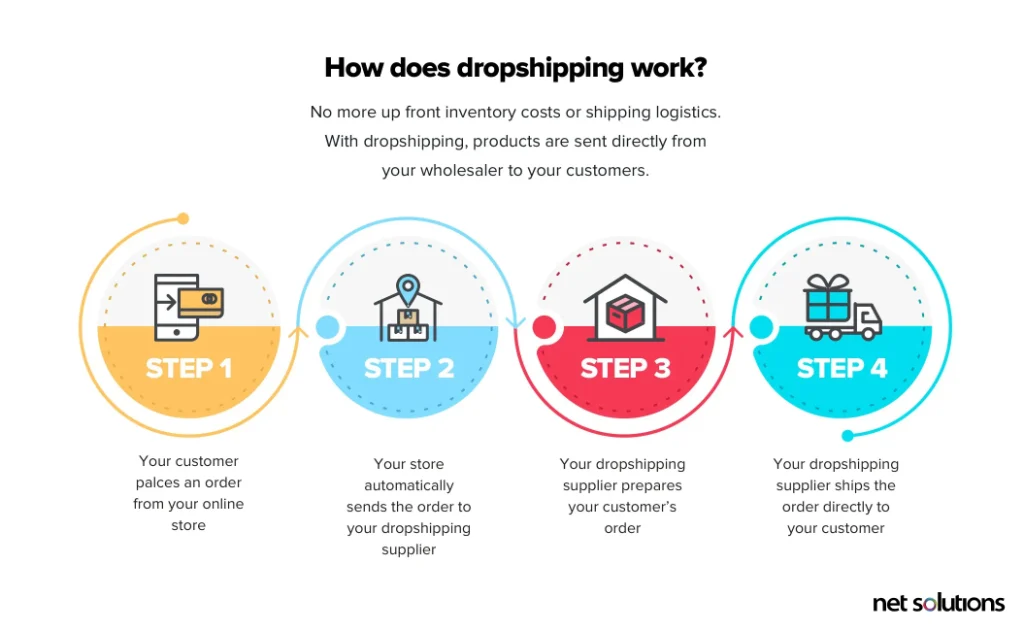
2. Dropshipping
In the Dropshipping model, you leverage third parties (“drop shippers”) to fulfill orders you collect as you collect them. This way, you can sell products without ever keeping them in stock. Spocket, Modalyst, and Pritful are popular dropshipping platforms.
3. Subscription model
In the subscription model, a company sells its products or services regularly, monthly, quarterly, or yearly.
In B2C retailing, subscriptions typically fall under three types: replenishment (convenience), curation (surprise products), and access (VIP products).
Popular subscription model examples are Dollar Shave Club, Blue Apron, and Birchbox.
Chapter 2Is eCommerce Applicable to All Businesses?
eCommerce, which involves the buying and selling goods or services, offers flexibility and can be adapted to various types of businesses. However, its suitability depends on the nature of products or services, target market, and business model.
- Nature of Products or Services: eCommerce would be ideal for
- Tangible products
- Digital products & services
- Service-oriented businesses
- Business to Consumer (B2C), Business to Business (B2B), and Business to Government: eCommerce is effective for B2C, B2B, and B2G models, although the strategies and platforms may vary.
- Customer-to-Customer and Customer-to-Business: eCommerce can work well for these two categories, where the consumer acts as the seller to other consumers (e:g Facebook Marketplace) or businesses (e:g Upwork).
- Global Reach: eCommerce is beneficial for those targeting global markets.
eCommerce allows businesses to scale and target niche markets. A few limitations of businesses that would find eCommerce an unsuitable option are personalized or customized services or products that are subject to regulations. Highly perishable goods or very bulky/large may be a challenge when venturing into eCommerce.
Chapter 3Ways to Develop an eCommerce Website
Building an e-commerce website involves developing different aspects of your store, including its functionality, payment processing, responsiveness, user interactions, and visual design. Crafting a well-designed website that offers customers a seamless experience is crucial for success in the e-commerce industry. You need to know how to get the right features, choose the right framework for development, and integrate features into a website template.
eCommerce website development can be done in three ways:
- Open source or build your website from scratch if you have the teams. This implies that you are responsible for PCI compliance, web hosting, security, and other issues.
- SaaS eCommerce solutions rely on the cloud. A third-party vendor builds the solution on the ‘cloud.’ Instead of building and developing yourself, you could rent a platform – in this case, the platform provider takes care of the hosting, updates, security, and PCI compliance.
- MACH architecture is preferred as businesses expand and scale. It goes beyond the traditional monolith structure and allows you to choose the technology best suited to your business needs and roadmap.
MACH architecture is especially suitable for organizations that want to transform or remain adaptable in a changing digital world. The components are:
Microservices implies developing software as a set of services. Each service runs in its process and communicates using mechanisms, usually through HTTP APIs.
API-first design approach treats APIs as components. It means that APIs are developed first and considered the means of interacting with a system or service.
Cloud-native refers to applications designed and created to run in cloud environments. This involves leveraging features and services such as managed databases, auto-scaling, and serverless functions.
Headless is an architectural approach in which we decouple the front-end presentation layer from the back end. It allows for greater flexibility and versatility. This approach is well suited for businesses as it enables experimentation with new technologies, allows better control, and makes software maintenance easy.
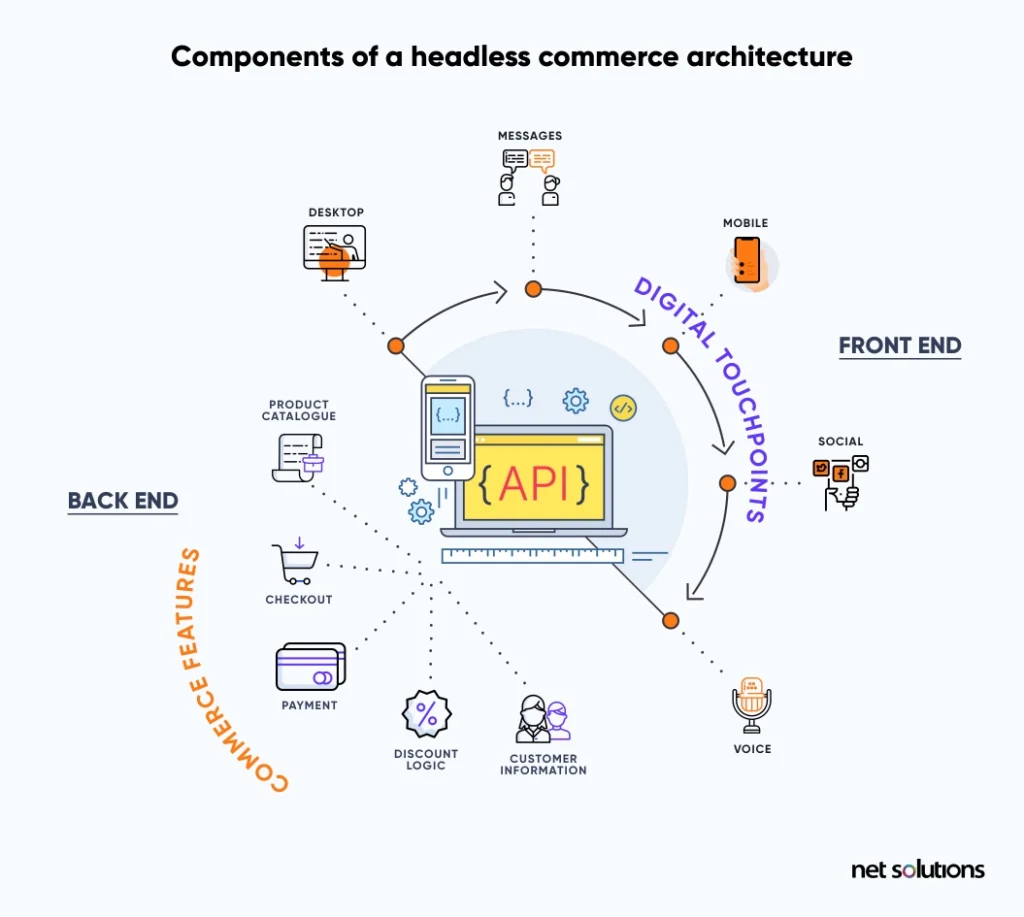
Taking the headless approach to eCommerce helps businesses create a speedy, more dynamic, and personalized customer experience.
Chapter 4eCommerce Website Accessibility
Website accessibility refers to designing and developing websites that allow people with disabilities to easily use them, ensuring all users can navigate and understand the website regardless of their cognitive abilities. Accessibility covers a range of disabilities, including auditory, physical, speech, cognitive, language, learning, and neurological impairments.
Some important aspects of website accessibility include:
- Compatibility with Screen Readers,
- Keyboard Navigation,
- Clear and Consistent Layout
- Text Alternatives
- Contrast and Color Usage
- Video and Multimedia Accessibility
- Scalable Content
- Error Identification and Recovery,
- Language and Readability
Following web accessibility guidelines like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) not only aids individuals with disabilities but also enhances the user experience. It can improve search engine optimization (SEO), expand the audience reach, showcase responsibility, and ensure compliance with obligations in numerous countries.
Chapter 5Selecting an eCommerce Platform
Once you understand the basics of eCommerce development, you can choose the appropriate eCommerce platform per your specific needs, business size, and technical expertise. If you’re aiming for a cost-effective, growth-oriented platform that helps you build above-par customer experiences, choose the right platform while keeping these factors in mind:
- Ease of Use with simple management tools, smooth navigation, intuitive interface
- Customization in layout, design, and functionality
- Scalability to adjust to increased sales & traffic
- Pricing Structure that balances the basic cost and the transaction fees
- SEO Friendliness to ensure the visibility and discoverability of products
- Secure Payment Gateways to protect customer data
- Insightful Analytics to understand customer data and other key metrics
- Mobile responsiveness for a seamless shopping experience
- Plugins and integrations for SEO, marketing, payments, and inventory management
- Community and customer support for assisting with technical issues and offering advice
It is always good to test a few platforms before you choose one for your product line.
Some of the most popular eCommerce platforms are Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Wix eCommerce, and Salesforce Commerce Cloud.
Chapter 6Magento Adobe eCommerce Platform
Magento Adobe eCommerce Platform (formerly known as Magento Enterprise Edition ) is one of the leading eCommerce platforms and offers a flexible solution for businesses of all sizes. It is an open-source platform built on PHP and MySQL, allowing extensive customization options to cater to business needs.
Features of Magento Adobe Commerce
- Scalability
- Smooth Performance
- High Customizability
- Detailed Catalog Management
- State-of-the-art Marketing Tools
- Smooth Integrations
- Robust Security
The advantages of selecting Magento Adobe Commerce are:
- Improved user experience and higher customer satisfaction
- Global reach for businesses
- Data-driven Insights on customer behavior patterns and sales trends
- Community support for troubleshooting and innovation
- Mobile responsiveness and a seamless shopping experience
Magento Adobe Commerce is a flexible eCommerce platform that can be tailored to suit your business needs. Its features and advantages make it an option for businesses looking to thrive and stand out in the competitive online marketplace.
Chapter 7 Exploring BigCommerce
BigCommerce is a powerful eCommerce platform that businesses of all sizes prefer for its capabilities and benefits.
- It simplifies enterprise eCommerce, and its user interface allows the setup and management of online stores without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
- You can use their native low code no code tools, your frontend solutions in headless design – or both in a multi-storefront environment.
- The platform excels in functionality and provides
- product management,
- efficient order processing,
- integrated payment gateways for transactions,
- flexible shipping options,
- scalability options,
- robust security,
- omnichannel sales,
- extensive app marketplace,
- impressive integration capabilities,
- connections with third-party applications and marketplaces,
- mobile responsive design,
- improving operational efficiency and expanding customer outreach,
- built-in SEO tools that enhance visibility by driving store traffic.
Chapter 8 Building your eCommerce Website with Shopify
Shopify is widely recognized as an eCommerce platform that empowers businesses, regardless of size, to create and manage stores effortlessly. Its user interface makes it accessible even for those with limited technical know-how, thus making it advantageous for businesses and aspiring entrepreneurs venturing into the world of commerce.
Shopify offers
- intuitive interface,
- an array of customized themes and templates,
- an app marketplace with various plugins and integrations,
- multi-channel selling,
- multi-lingual settings,
- abandoned cart recovery,
- dropshipping,
- scalability,
- smooth hosting services,
- PCI compliance and robust security measures,
- customer relationship management (CRM),
- an integrated payment system called Shopify Payments,
- analytics tools and reporting.
Chapter 9eCommerce Replatforming
In a landscape of technology advancements and evolving customer preferences, eCommerce businesses face immense pressure to stay competitive. No business can afford for legacy systems to hinder or slow down growth.
“To survive in the current business environment, you have to be able to take advantage of evolving technology trends, and the one thing that’s been constant the last 10 years—and I believe will continue to be constant the next 20 or 30 years—is that technology is going to continue to change at a rapid pace.”
― Stephen Orban, Ahead in the Cloud: Best Practices for Navigating the Future of Enterprise IT
To capitalize on opportunities for omnichannel commerce, microservice-based solutions, and enhanced scalability, retailers turn to eCommerce replatforming as a quick solution. This allows them to switch to eCommerce platforms that align with their evolving needs and offer customers seamless experiences.
eCommerce replatforming entails modernizing an eCommerce website while avoiding a complete rebuild. It involves transferring the design, data, and essential functionality from one eCommerce platform or technology stack to another and configuring, optimizing, or adding desirable features.

Chapter 10Product Recommendation Engine
Product recommendation systems are tools in the marketplace that enhance user experiences and drive sales through personalized and relevant product suggestions based on various types of customer data. This data includes wish lists, shopping carts, viewed items, search history, preferences, and past purchases.
There are three product recommendation engine categories:
1. Collaborative filtering examines customer data to predict and suggest products that may interest an individual. It leverages the knowledge and preferences of the user community to provide recommendations.
2. Content-based filtering creates a preference profile for each customer based on their tastes and provides recommendations accordingly. It’s often used behind suggestions like “Since you bought this, you’ll like this.”.
3. Hybrid recommendation systems combine the capabilities of both filtering and content-based filtering. They utilize data from groups of users, individual users, and past preferences to deliver tailored product recommendations.
Product recommendation systems are widely utilized across industries, like e-commerce, social media, and streaming services. They boost eCommerce sales and enhance user satisfaction by suggesting products based on location, seasonality, price range, and user behavior.
Chapter 11Product Information Management (PIM)
For a seamless eCommerce experience, streamlined product information management (PIM) holds immense value.
(PIM) implies organizing and managing product data across different systems and channels. As businesses expand, the complexity of handling product information grows, making handling attributes, images, descriptions, and supplier details challenging. Cloud-based PIM software is a hub for storing and maintaining product information.
The Product information management (PIM) software operates in three stages: collection, sorting, and distribution.
Investing in a product information management system helps address challenges such as maintaining accurate and consistent product information across channels and, eventually, enhancing the customer experience. However, before committing to a PIM software investment, businesses must carefully assess their needs and growth trajectory.
Chapter 12Voice Search for eCommerce
Voice search is a technology that enables users to search the internet by simply speaking to their devices, be it a smartphone, computer, or smart speaker. It utilizes voice recognition capabilities to comprehend the user’s instructions and promptly provides search results through verbal responses or displays them on the screen.
Voice search is significantly transforming the eCommerce customer journey, providing a more intuitive and efficient way for consumers to interact with online retailers.
Value addition through voice search:
- Enhanced Customer Experience
- Personalized Shopping Experience
- Time Efficiency and Ease of Use
- Smart Shopping and Improved Search Engine Results
Voice search is a powerful tool in the eCommerce landscape, offering numerous benefits. As this technology continues to evolve, eCommerce store owners must adapt to these changes to stay competitive and meet their customers’ dynamic needs and preferences.
Chapter 13eCommerce Personalization
“If you do build a great experience, customers tell each other about it. Word of mouth is very powerful.”
― Jeff Bezos, Amazon
eCommerce personalization involves customizing online shopping experiences for individual customers through relevant suggestions related to content, product recommendations, offers based on preference, behavior, and demographics, and advertisements. These suggestions are based on a customer’s previous purchases, browsing behavior, geographic location, language, and other personal information.
eCommerce personalization aims to build customer loyalty, increase satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) help track customer behavior and offer individualized experiences. It helps a business be transparent about how it uses customer data. Prominent examples of eCommerce personalization are Netflix and Amazon.
Chapter 14eCommerce Security
Technology adoption, borderless eCommerce advancements, payment processing systems, and evolving consumer behaviors have all contributed to an upward trend in eCommerce. However, this surge in eCommerce activities has also resulted in a rise in cyberattacks.
These are the types of security threats that commonly target eCommerce platforms.
- Financial fraud occurs when deceptive practices are employed during transactions to gain personal benefits.
- Social engineering involves tactics to gain access to systems or sensitive information.
- Phishing attacks deceive users into revealing data or downloading viruses and malicious programs.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm websites with traffic volumes, while brute force attacks rely on trial-and-error methods to guess passwords or passphrases.
- SQL injections exploit database vulnerabilities to steal or erase data, while cross-site scripting (XSS) techniques use user information from websites.
- Additionally, e-skimming poses a threat by capturing individuals’ financial and personal details without their knowledge.
To ensure the security of your eCommerce site, opt for a platform such as Magento, WooCommerce, Shopify, BigCommerce, or Squarespace. Implement HTTPS with SSL/TLS protocols to encrypt and authenticate data transmission.
Chapter 15PCI Compliance
PCI compliance is necessary for businesses that process credit cards, including eCommerce merchants, payment processors, and service providers. It guarantees all credit card payments’ storage, processing, and transmission.
Credit card companies have established the PCI DSS Compliance standard to minimize the risks associated with data breaches and fraudulent activities. It also contributes to building a brand image.
PCI compliance is relevant for:
- Service Providers: who handle cardholder data storage, processing, and transmission on behalf of companies
- Merchants: who directly accept credit card payments for goods and services sold online.
PCI compliance is especially critical for eCommerce platforms and software development. Major eCommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, and BigCommerce mandate that all developers adhere to PCI compliance standards. PCI compliance is also crucial in software development, such as SaaS products.
Chapter 16eCommerce Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is the behind-the-scenes process in eCommerce involving receiving, packaging, shipping, and delivering products to customers. It also includes handling exchanges and returns. Businesses work to speed up order fulfillment time to provide a shopping experience, even though it can increase expenses. The order fulfillment process consists of six steps:
- inventory receiving,
- organizing inventory,
- picking items,
- packaging them securely,
- shipping them out,
- processing exchanges or returns.
Various order fulfillment methods are available, like third-party fulfillment, merchant fulfillment, and drop shipping. Order volume, eCommerce platform, geographic location, and delivery time should be considered to determine an order fulfillment strategy.
Chapter 17A Typical eCommerce Customer Journey
eCommerce is about satisfying your end-user, which implies knowing your customer’s entire journey.
An eCommerce customer journey analyzes how customers interact with a brand across platforms, channels, and touchpoints. It encompasses all their interactions, from discovering the brand to their experience with its product.
Customer journey mapping gathers data on what delights or disappoints customers and how to enhance the overall user experience.
The customer journey consists of Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Loyalty/Advocacy.
Best Practices for eCommerce Customer Journey Mapping
- Build detailed customer profiles
- Develop a visual representation of touchpoints
- Utilize data from various sources (emails, surveys, interviews)
- Create user personas
- Study customer referral paths
- Focus on customer needs
- Tailor your products, offers, and content as per customer needs
- Monitor and modify regularly
Chapter 18Top eCommerce KPIs
An eCommerce Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a value that assists businesses in tracking and evaluating the success of different aspects of their operations. These indicators are utilized to assess an eCommerce business’s efficiency, effectiveness, and profitability, providing insights into how it’s achieving its objectives.
Some commonly used eCommerce KPIs include:
1. Conversion Rate measures the proportion of website visitors who make a purchase.
2. Order Value (AOV) represents the amount customers spend per order.
3. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the expense incurred in acquiring a customer. This includes the marketing and sales costs.
4. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) estimates the total value a business can expect from a customer account through its relationship with the company.
5. Cart Abandonment Rate is the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart but do not complete the purchase.
6. Traffic (unique visitors) indicates the number of individuals visiting a website, which is crucial for understanding the website’s reach and evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns in generating traffic.
7. Return on Investment (ROI) for Marketing Campaigns measures the profitability of marketing campaigns.
8. Retention Rate is the percentage of customers who return to make purchases.
Monitoring these and other relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) helps eCommerce businesses make data-based decisions, optimize operations, and improve performance. B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) eCommerce will use different KPIs.
Chapter 19eCommerce Challenges and Solutions
In a rapidly evolving online market, eCommerce businesses face many challenges. Below is a snapshot of the significant challenges and the corresponding solutions.
| eCommerce Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Intense Competition |
|
| Inventory Management & Supply Chain |
|
| Website Visibility & Traffic |
|
| Technological Advancements and Integration Challenges |
|
| Data Privacy & Security |
|
| Customer Experience and Retention |
|
| Customer Expectations |
|
| Cart Abandonment |
|
| Scalability and Global Expansion |
|
To tackle these obstacles, e-commerce companies must be flexible, customer-centric, and well-versed in technology. It is crucial to stay updated on industry trends and advancements while constantly improving and customizing the shopping experience to excel in e-commerce.
Chapter 20Why Your Business Needs Mobile eCommerce Apps
Mobile commerce sales are expected to account for $710 billion in commerce sales by 2025
― Forbes
Having an eCommerce app can bring the following advantages to your eCommerce business:
- Improved Accessibility
- Enhanced User Experience
- Increased Customer Engagement
- Improved Sales
- Valuable Data Collection
- Building Brand Loyalty
- Competitive Edge
- Integration with Social Media
- Cost-Effective Marketing
- Offline Access
Mobile eCommerce apps tremendously enhance the shopping experience for customers, drive increased sales, and provide insights for businesses. They have become a component of digital commerce strategies. You can measure their success by tracking key performance indicators like downloads, time spent on the app, and revenue.
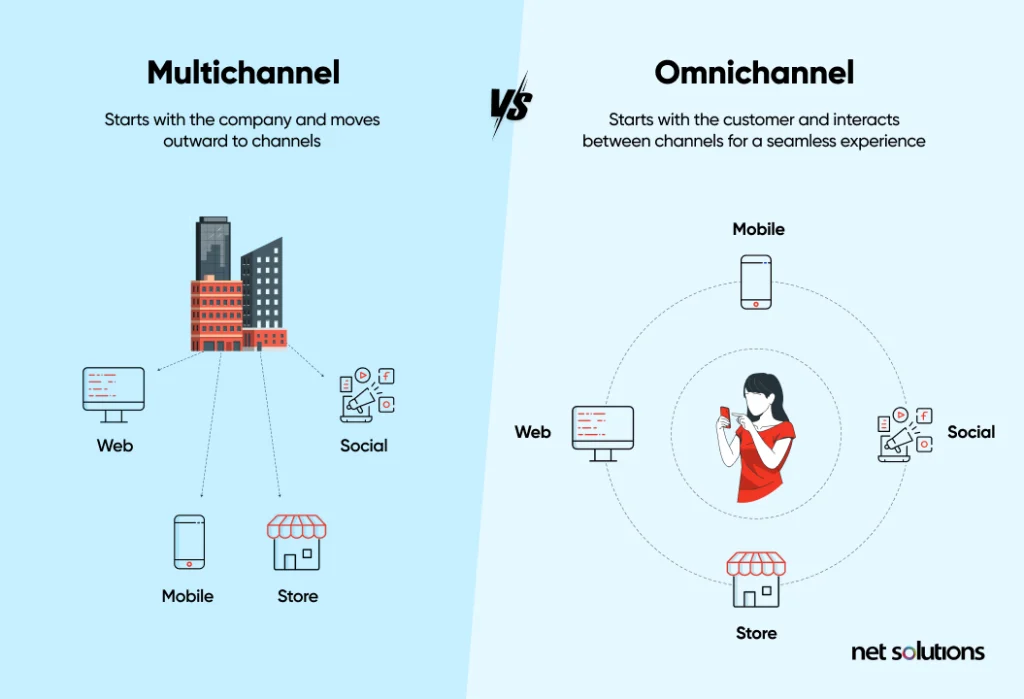
Chapter 21Omnichannel Strategy and How it differs from Multichannel
eCommerce is about bringing more users to your website and retaining them as customers. An omnichannel strategy provides a seamless, personalized, and interconnected experience. Not only does this bridge the online and offline purchase points, but it also enhances brand recognition, gives a competitive edge, and increases revenues.
As an eCommerce business, you can improve its omnichannel strategy with the following steps:
- understand the customer
- integrate channels
- create consistent branding and messaging
- leverage technology
- personalize customer interactions
- maintain a flexible and agile approach
- use data and analytics to optimize the strategy
Understand also that omnichannel strategy is very different from multi-channel strategy. A multi-channel retail strategy allows the customer to buy products from all channels that are separate purchasing touchpoints – these are not interconnected. Many businesses start from the multi-channel strategy and move on to omnichannel retail solutions.
Chapter 22eCommerce Trends
In a constantly evolving and technologically advancing business environment, chances are you will struggle to sustain if your business doesn’t proactively adapt to changes or follow trends. Now that you have a fairly good idea of how eCommerce functions, keep in mind the following trends for 2024.
Even though retail sales have been around, eCommerce is constantly evolving. Staying updated on trends is crucial to staying competitive and finding strategies that work for your brand and business model. It’s important to monitor what your competitors are doing and make changes that will positively impact your profits.
To implement these changes, you need a partner who understands the intricacies of your business and your customers’ needs. Net Solutions is a trusted company that has worked with names in retail like Euro Car Parts and 2XU. We have successfully built and improved (migration and replatforming) eCommerce websites, helping them stay competitive during international expansions and adapt to the ever-changing industry.
SHARE THIS POST
Table of Contents
Related Services
Related Resources
- eCommerce App Development Cost: Budgeting In-Depth Guide
- 13 Differences Between B2B and B2C eCommerce Websites
- Top 10 eCommerce Challenges and Easy Ways to Overcome Them
- 3 Types of eCommerce Business Models That Work in 2024
- eCommerce for Business: Is eCommerce Applicable for All Business Types
- eCommerce Customer Journey Mapping - The Secret to Higher Conversion Rates
- What is Headless Commerce? The Ultimate Guide
- Top 15 eCommerce KPIs to Track the Performance of Your Online Business
- Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce App
- Omnichannel Retail Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide
- Omnichannel vs Multichannel Retailing: The Complete Guide
- What is eCommerce Order Fulfilment? (And 6 Steps to Improve the Process)
- PCI Compliance: Everything You Need To Know
- The BEST Guide to eCommerce Personalization
- 12 Essential Factors for Choosing the Best eCommerce Platform
- The Ultimate Guide to Product Information Management (PIM) Systems for Ecommerce
- What is a Product Recommendation Engine (And How it Helps Boost Sales)
- eCommerce Replatforming: Challenges, Benefits, and Best Practices
- The Ultimate Guide to eCommerce Security
- Top 13 eCommerce Trends in 2024
- How Voice Search will Transform the Future of eCommerce
- What is Web Accessibility (And Why it Matters for Your eCommerce Business)



