Summary: The software development life cycle and software development process are both essential to creating product-market fit software. While most assume these terms are the same, many differences exist. Read on to understand the critical differences between a software development life cycle and process, and learn about some of the best software development process practices for 2022 and beyond.
“If you fail to plan, you’re planning to fail.” – Benjamin Franklin.
It’s okay to be spontaneous on vacation or while getting a tattoo, but spontaneity doesn’t always work when building software. A clear and well-defined software development process is essential. Otherwise, you’ll see a delay of months or years.
A well-defined process is a key to building excellent software and is an integral part of the software development lifecycle. It ensures fast and quality delivery.
However, there is much more to a software development process and software development lifecycle that one needs to understand before taking on software development projects.
In this blog, we will understand both these concepts better but first, let’s begin with the basics.
What is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
Software development life cycle (SDLC) is a series of stages a software passes through during its lifetime. It offers us an overview of what it takes to create software.
We can equate it to the recipe you follow to bake your favorite cake. If the first step is to combine flour with cocoa powder, you’ll have to follow the process to ensure a finely baked cake. But, if you only mix the mentioned ingredients in one go, the cake will not be worth relishing.
The same goes for the software development life cycle — there is a defined step-by-step process for creating quality software. The software development efforts will go to waste if you miss any steps or follow them haphazardly.
The software development life cycle comprises requirement gathering, design, development, test, deployment, and maintenance. Each software development stage is handled by a dedicated team of professionals with expertise in the niche.
SDLC stages mostly stay constant no matter what software development methodology we follow. However, the approach towards implementing these stages changes with changing development methodology.
Prevalent software development models include Waterfall, Spiral, feature-driven, Agile, Lean, Rapid Application Development, and Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe).
Related Article: Top 7 Software Development Methodologies: Pros & Cons
For instance, in the traditional methodology such as Waterfall — all the mentioned stages are sequentially followed while restricting backward movement. On the other hand, the Agile software development process model follows an iterative approach where the teams can go back to a previous stage to fix a bug or accommodate a new requirement.
Why is Software Development Life Cycle Important?
SDLC can assist you in easing your product’s entire software development journey. Here’s how the SDLC process adds value to your software development ventures:
- Faster time to market — the development and the turnaround time get relatively shortened
- High-Quality software — the process follows synchronous steps to development, leaving low scope for bugs and inconsistencies
- Facilitates management control — whether it is a small or a large project, the SDLC model offers project management control to help them visualize and track development progress
- It brings the development team on the same page — when every team member understands the stages of the software development life cycle, they know what they can expect and how to plan for what’s next.
- Breaks existing silos among the teams — the SDLC phases introduce full-swing communication among the development teams by tying them up with a process that requires collaboration
- A clearer perspective of roles and responsibilities — Each SDLC phase has a clearly defined intent. Thus, each team member knows their role in the software development life cycle.
What are the Six Phases of Software Development Life Cycle?
The below measures will help you get a grasp on the SDLC methodology. Let’s walk through the SDLC steps to get an overview of the process:
1. Planning and Requirement Gathering
The client defines a problem that needs to be solved, which further forms the basis for finalizing the requirements. We gather all the information from the client and users (if required) to create requirement documents so that the development team understands what they are building.
Then follows planning, which includes distributing work across teams, setting milestones, creating timelines for delivery, getting cost estimates, conducting a risk analysis, and devising a plan to mitigate the risks.
Creating a proof of concept is also part of this stage, where the technical feasibility is checked and validated before proceeding with the development work.
2. Design
The design phase of the software development life cycle focuses on creating software architecture, prototypes, and user experience design. Here’s an overview of what these activities entail:
Software Architecture: Refers to creating an organized flow of elements in a software code for quality assurance, clarity, and accessibility. You can refer to software architecture as the blueprint for the development team.
Prototype: The UI/UX team builds a prototype version of the software to validate its look and flow of design elements. It lets the development team and the stakeholders visualize the overall look and feel of the software.
3. Develop
In this SDLC phase, coders work on bringing the concept into reality. The developers create KLOCs (thousands of lines of code) using programming languages they feel comfortable with.
The development team aims to achieve developer velocity while ensuring quality delivery.
The development team might release the software in one go, as with waterfall development, or can choose to deliver software in fragments (segmented into features, i.e., Agile development).
Once the code is ready, the development team shares it with the testing team for review.
4. Testing and Quality Assurance
This application development life cycle phase focuses on testing the written code for bugs and other inconsistencies. The testing and quality assurance team works to test and report the bugs to the development team.
The testing team can rely on manual or automated testing (per their expertise and defined process).
We can say that the testers and the development team work together to ensure foolproof software delivery.
5. Deployment
The entire software or a part of it goes into the production environment phase after developing, testing, fixing, retesting, and validating. If you follow the Agile SDLC process, deployment could be the launching of MVP and other features. However, in the case of Waterfall, deployment refers to launching a fully-fledged product in the market.
If the end-users experience any issue with the software, it moves back to the software development team for reconsideration and fixing.
6. Maintenance
New requirements will likely drop with new technologies and changing user requirements. The software development team needs to iterate through the entire software development life cycle to accommodate these requirements to work on the recent change.
Thus, maintenance implies that software requires updates from time to time, which you must frequently do to uphold the software’s value proposition.
The common types of maintenance include:
- Corrective Maintenance
Removing the existing bugs from the software to improve its performance. These errors come to light, generally through user reviews. - Perfective Maintenance
New requirements keep evolving from time to time. And, to stay relevant and valuable, the software needs to be updated to accommodate these changes. That is the idea behind perfective maintenance.
Software Development Life Cycle Example — Soaq Case Study
Soaq is enterprise-level video software that prioritizes employee engagement. Net Solutions helped build the platform by sticking to the following stages of the software development life cycle:
1. Discovery (Requirements Gathering)
A business analyst, a project manager, a user experience analyst, and a technical architect were assigned to meet the Soaq team and understand their requirements and the scope of the product.
The results of the discovery phase included:
- Documentation of Requirements: We created an excel sheet that clearly and comprehensively listed all the Soaq team’s requirements.
- Proof of Concept (PoC): A proof of concept was created to validate the idea’s technical feasibility.
2. Design (Design Framework, Application Architecture, and Prototype)
At this stage, a design framework, software architecture, and a prototype were created. Each phase included:
a. Design Framework
Teams: Business analysts and UX team.
The design framework included a collection of screen mockups for every stage of the user experience journey. This included a flowchart that helped visualize where each user-driven click leads.
b. Software Architecture
Teams Included: Technical Architect, business analysts, and the UX team
A software architecture, i.e., the blueprint of the software, was created at this stage. The 3rd party integration, server requirements, database, and browser-related requirements are finalized at this stage.
3. Development
We followed the Agile software development life cycle to develop the enterprise software according to the approved UX design and technical specifications. Our focus on this part was to
- Conduct daily stand-ups to ensure transparency of the process and track the team’s progress
- Work in time-boxed sprints to work on prioritized features
- Build and launch an MVP (Minimal Viable Product) that focuses on should-have features of the product
- Wait for feedback and re-iterate through the software development life cycle to accommodate the changes while we work on new features side by side.
Then followed Agile testing (manual and automated tests), deployment (launching MVP), and continuous improvement (adding new features and fixing reported bugs).
Soaq’s collaboration with Net Solutions resulted in the world’s first intelligent, widely-adopted enterprise video solution, which made Gartner’s 2018 List of Cool Vendors in Content Services.
For an in-depth analysis, here’s the complete case study:
What is a Software Development Process?
A software development process is a series of steps we execute in each phase of the software development life cycle that leads to a specific output.
Software Development Process Example:
Let’s consider the Requirement Gathering process in the Planning & Requirement Gathering phase of the SDLC:
- Conducting interviews, surveys, and brainstorming sessions to understand the primary business pain.
- Questioning assumptions & removing the language ambiguity.
- Identifying and discussing different use cases.
- Writing user stories for all required use cases.
- Creating Demo for each user story to demonstrate to the developer and the client that the requirement has been met.
All these steps represent what it takes to gather project requirements from the client under the SDLC methodology. This process is a part of the Planning & Requirement Gathering phase, which includes risk analysis, cost estimation, and proof of concept.
Types of Software Development Processes
Many software development processes have been formalized to tackle complex projects efficiently. Choosing the right one depends on factors like project size, your team, and your end goals.
For a better overview, let’s compare five types of software development processes and their advantages and disadvantages.
1. Agile & Scrum
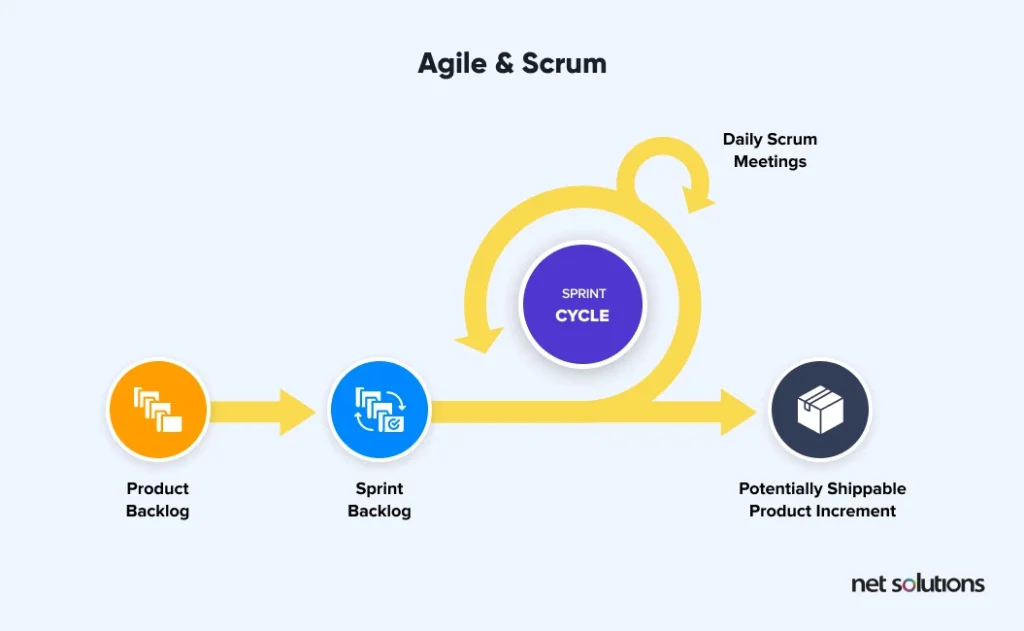
As opposed to the sequential approach of the waterfall process, the agile approach and its methodology Scrum follow an iterative and dynamic approach to development.
In the agile software development process, cross-functional teams work in sprints lasting two weeks to two months. The goal behind each sprint is to release a usable feature in the designated time.
Here are the steps in the agile and scrum software development process:
- Product Backlog
- Sprint Backlog
- Sprint (Design & Develop)
- Release working feature
- Feedback and validation (add to backlog)
- Plan next sprint
The agile approach moves fast, releases often, and caters to user needs instead of following a rigid documented procedure. Therefore, it becomes easy to incorporate user feedback throughout the development process.
However, things can quickly go haywire in agile & scrum if there is no collaboration and communication between the cross-functional teams.
When Should You Use Agile & Scrum?
The agile software development process is the best if you have a dynamic team working on a project that requires continuous updates.
However, you should avoid it if you have a resource-strapped team with a tight budget and a strict timeline. The dynamic nature of the agile process may result in product delays or conflicts with the existing architecture.
2. Incremental Development
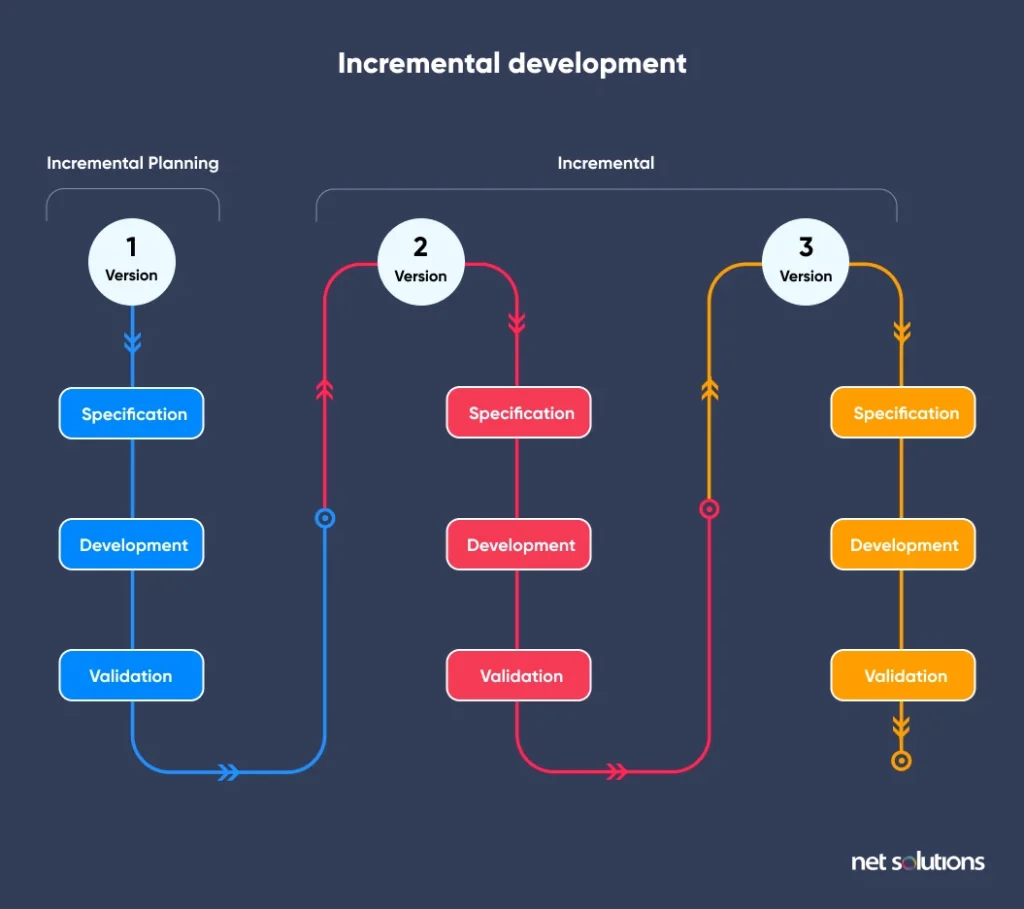
The incremental software development process is a middle ground between traditional Waterfall and agile approaches. Here, we develop software in small parts and test each piece individually with users for feedback.
Each increment in the incremental development process adds a new feature. An example can be creating an MVP featuring only the core function and adding new features based on user feedback.
Here is how the process flows in the incremental software development process:
- Specifications
- Development
- Validation
Incremental software development is less expensive. Also, it is easy to incorporate sudden changes. However, the process can be time-consuming and requires a lot of planning.
When Should You Use Incremental Development?
The incremental software development process best suits teams with precise project requirements and more flexibility. However, teams with a clear long-term technology plan should avoid this approach.
3. Iterative Development
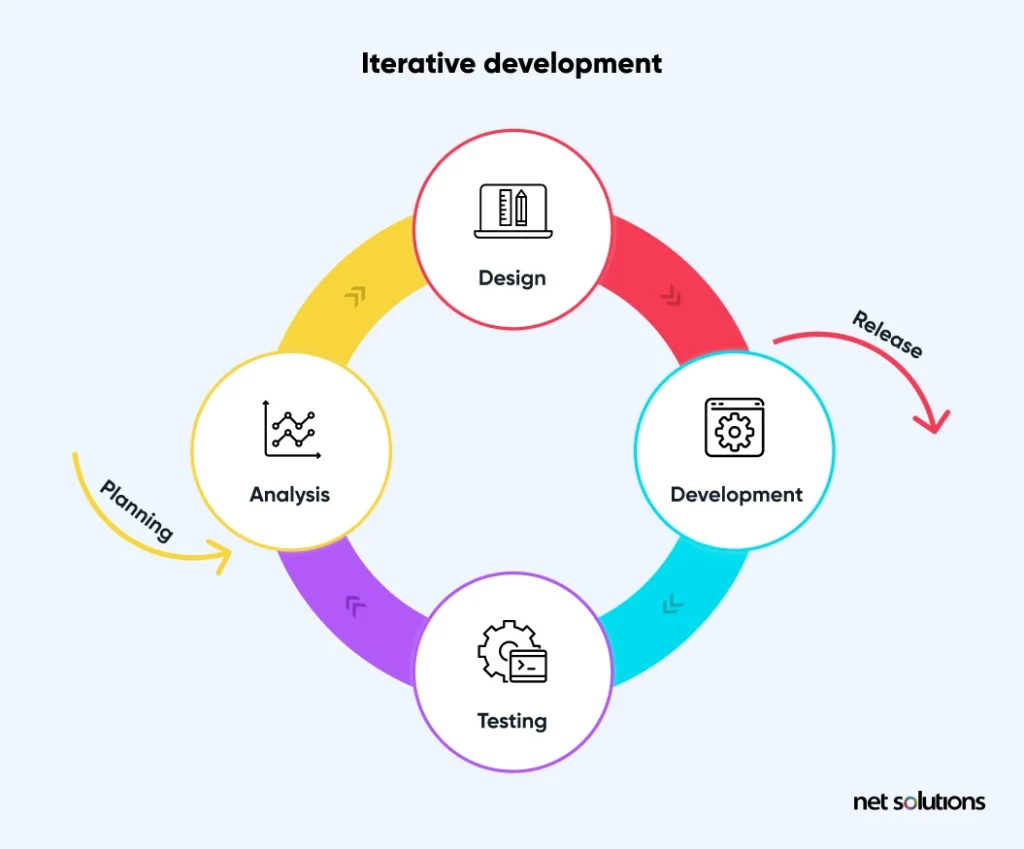
The incremental development process also follows the mix of Waterfall and agile development approaches. The only difference is that we develop a product version with all features and functionalities and release it in the market for user feedback. Then, based on the received feedback, we can upgrade the product features.
This way, the software evolves with each version, and we reach one step closer to the final version. Here are the steps in the iterative software development process:
- Analysis
- Design
- Development
- Testing
As the iterative approach focuses more on design than documentation, we can build products faster. Also, we can have an idea of how your product will look right from the beginning. However, the process is expensive and may need a lot of resources.
When Should You Use Iterative Development?
You should use an iterative development process if your team knows the project requirements and has clear long-term technology goals. Otherwise, it’s not a good approach for you.
4. V-shaped Planning
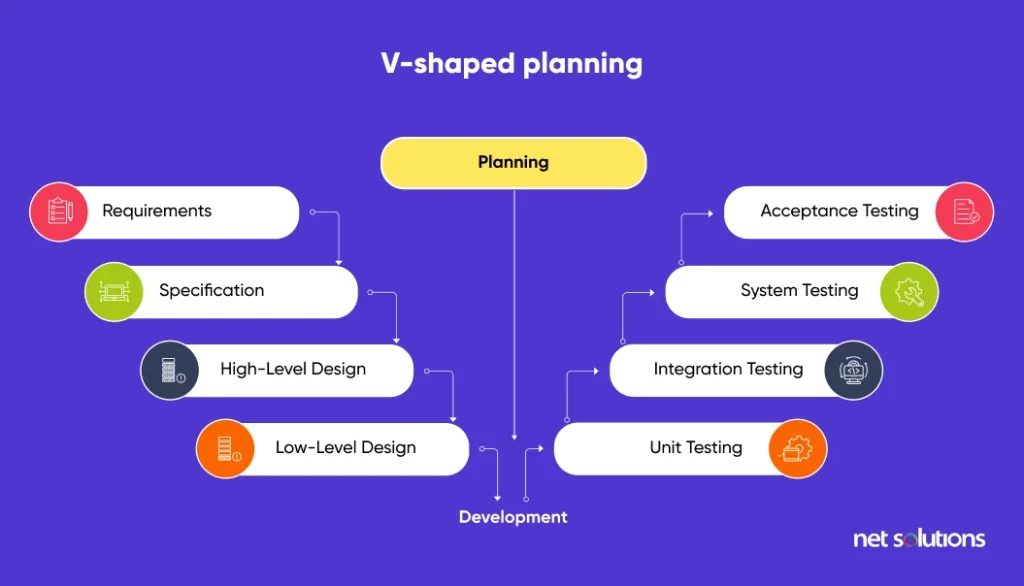
V-shaped planning is an enhanced take on the classic Waterfall process that aims to reduce its biggest downfall, the lack of testing.
The approach is simple. Instead of following all the steps in sequential order and saving testing for the end, we follow strict validation and verification at the end of each stage. This way, we aim for total quality management in software development.
Here are the steps we follow in V-shaped planning:
- Requirements
- Specifications
- High-level design
- Low-level design
- Development
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- Acceptance testing
When Should You Use V-Shaped Planning?
V-shaped planning is best if your team works on a small product with precise requirements. However, if you want flexibility and early input from users or the conditions are unclear, V-shaped planning is not for you. It will be challenging to lay out a clear plan without precise requirements.
5. Spiral Planning
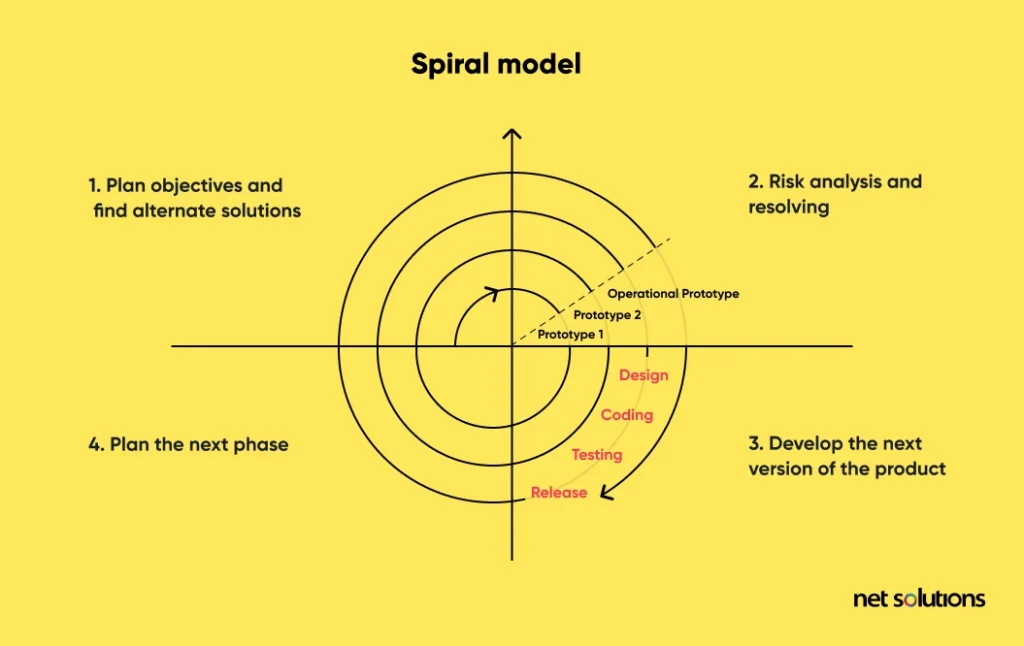
In Spiral Planning, we combine testing-oriented V-shaped planning with the flexible nature of iterative, incremental, and agile development processes. The idea is to reap the benefits of both top-down and bottom-up development approaches.
Here are the basic steps in the Spiral planning software product development process:
- Planning
- Risk Assessment
- Development and validation
- Evaluate results and plan the next “Step.”
Spiral Planning emphasizes risk assessment and dividing the entire development process into phases. Therefore, it can help you more accurately plan and budget your project. Also, it is possible to involve customers in the exploration and review steps of each cycle.
However, in Spiral Planning, we need many people with a strong background in risk analysis. Besides, it is impossible to repurpose every project’s approach as it is highly customized.
When Should You Use Spiral Planning?
You should use Spiral Planning if your team is working on a large project and the requirements are unclear. It is also best to introduce a new service/product where you don’t want to take the risk.
6. Waterfall
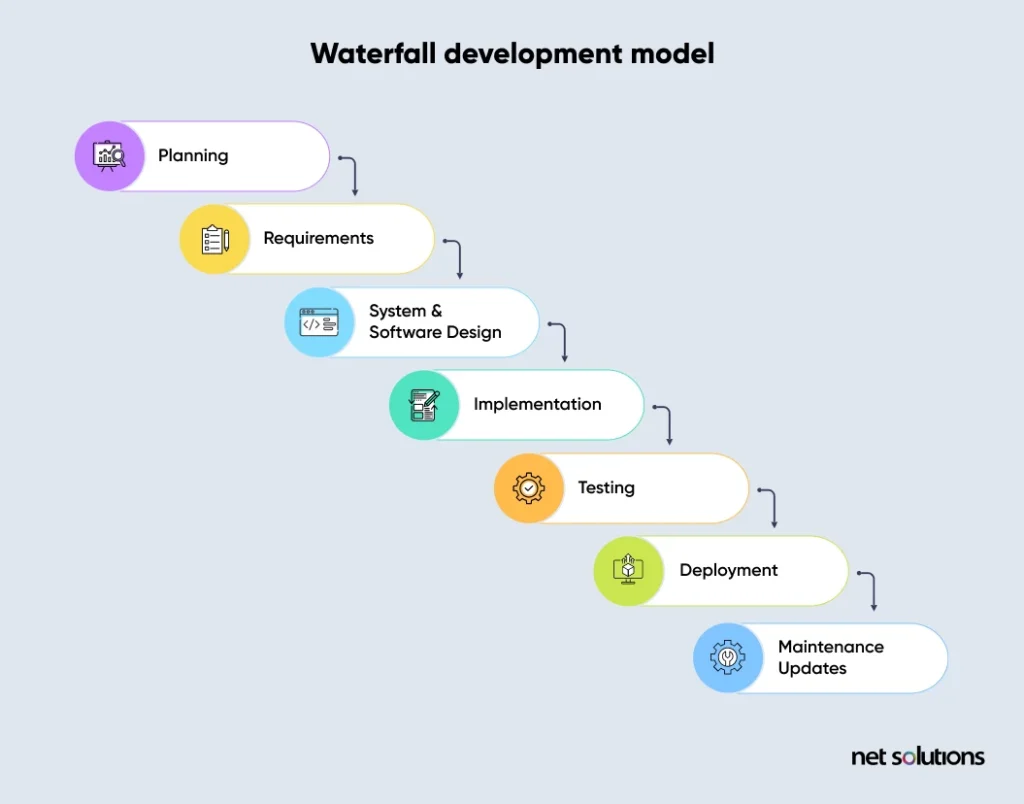
Also called the linear sequential model, Waterfall is the most traditional software development process. In this approach, we follow all the steps of the software development process in sequence. Finishing one step is essential before we move to the next one.
Here is how the software development process flows in the Waterfall approach:
- Planning
- Requirements
- System & Software Design
- Implementation
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance/Updates
Since the Waterfall approach involves a lot of planning and documentation, it is easy for the development team to understand and use it. However, the Waterfall process is expensive, and changes often take time. The approach also involves risks as changes are costly.
When Should You Use the Waterfall Approach?
The Waterfall software development process is best suited if you want to follow a rigid, documented approach where your goals, requirements, and technology stack are unlikely to change.
However, the waterfall is not the right option if you release a new product and need user feedback throughout software development. You should also avoid it if you want your development process to be more flexible and dynamic.
Difference between a Software Development Process & Software Development Lifecycle?
People often confuse the software development process with the software development lifecycle and vice-versa. They use the terms interchangeably. However, research shows several key differences between the software development process and the software development lifecycle. Let’s look at them:

Best Software Development Process Practices in 2022 & Beyond
1. Make Your Code Simple & Readable
Software development is a long game. Some projects last for years, and many team members switch the organization. After a few years, there are fewer chances that the original developers will still be around the corner.
A complex code will create problems for the new development team members as they have to spend significant time understanding the code. That’s why you should focus on maintaining a clean code. It is simple to read and easy to manage. New developers on your team can quickly get on the project even if the original developers are no longer available to guide them.
2. Test Early and More Often
Mistakes can happen right from the beginning of the software development process and sometimes be hard to identify. Sometimes we overlook issues until they become a significant problem, and resolving them takes time and resources.
That’s why you should test early and often. Not only will it save you effort, but you will also have enough time to fix these issues and get back on track.
3. Use Version Conto Track Changes
Tracking changes in small projects is easy, but tracking them in a large project with millions of code is impossible. That’s why you must use version control. Not only would it help you know what changes have been made in the code, when, and by whom, but it also ensures everyone in your team is working on the correct version.
4. Gather Continuous Feedback
Feedback loops are crucial in the software dev process. Unless someone points out the shortcomings in your product, you can’t improve. You must consistently and constantly listen to your customers during the software development lifecycle. Continuous feedback reduces unnecessary risks, delivers quality features faster, and ensures you release the right product into the market.
5. Follow the Continuous Integration Approach
We must also follow the continuous integration approach to allow developers to regularly merge their code changes into a centralized repository where we conduct automated tests.
The approach has two advantages:
- It keeps the software functional.
- It also automates the development and reduces the tedious task of writing and integrating code.
Besides, you always get an alert from continuous integration tools when there are errors. This way, you can ensure you are developing software faster without worrying about issues.
6. Break Your Project into Simple, Achievable Milestones
Large projects can be tiring both for the client and the software development team. Frustration starts building up when timelines stretch for several months and no progress is visible. That’s why you must break your project into simple, achievable milestones. It will keep your team’s morale high, avoid stress, and ensure you can efficiently manage your project’s progress. Moreover, there will be no gold plating or overly-stretched timelines, which is one of the primary reasons software projects fail.
7. Share What You Learned Across the Team
Knowledge-sharing is the key to an efficient software development process. When you share your learnings across the team, it not only deepens your understanding but also fosters collaboration across the team. By helping each other, you grow together and become more productive. Knowledge-sharing also acts as a point of reference for team members who will join you in the future. So, encourage knowledge-sharing across the team. The best approach will be to create a knowledge base where everyone can contribute their learnings.
Common SDLC Challenges & Solutions
Software development can be intimidating at times. You might not even realize when things spiral out of control and the project becomes a nightmare. Hence, it’s essential to be aware of common SDLC pitfalls and know how to avoid them.
Here are the common SDLC challenges and possible solutions:
Challenge 1: Lack of Clear Communication
Communication is integral to software development. Without it, unnecessary delays and costly mistakes can happen. Sometimes, the entire project may get derailed just because your team members were not actively communicating and continued working without being aware of the problem. Hence, ensuring clear communication within your team is a significant concern.
Solution
Encourage communication within your team. Every member should know their role, expectations, and how it aligns with their ultimate business goal.
Challenge 2: Late Requests from the Client
Sometimes, clients request a feature later due to a change in their vision, which has severe implications for the team—frustration and pressure build among the team, and productivity hampers.
Solution
While you can’t avoid this problem, you can mitigate it by gathering all the initial requests. You must also inform the client about the implications of having late submissions.
Challenge 3: Limited Time for Testing
Testing is crucial in software development. Despite this, there are times when teams lose time for testing. It can happen due to budget constraints or the pressure to deliver faster.
Solution
While preparing the time estimate for your project, allocate enough time for software testing. Also, start testing as early as possible so that you have ample time to identify and fix issues if they arise.
Challenge 4: Improper Allocation of Tasks
While people have understood the value of collaboration in software development over time, some members of your team might want to play the hero. They might want to pull the higher number of shifts or move heaven and earth to complete the project faster.
This practice looks good ideally, but it is often counterproductive. One person’s habit of playing the hero often puts extra pressure on the other members, and sometimes you miss out on crucial aspects. The entire team loses because one person desperately wants to win.
Solution
Allocate tasks and responsibilities wisely. Play with each person’s strengths and specialties. You have to grow and succeed as a team. Also, be cautious when assigning two projects to one person. The results may not be as expected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Without a software development process – you can quickly lose track, exceed budget, and surpass timelines. A software development process can help you streamline your project, offer the right direction, and always keep you on track.
A software process model is a simplified representation of a software development process, and we use it to explain different software development approaches.
- Keeping up with technological advancement and knowing how to leverage new trends in software development.
- Incorporating new and complex features in an application ensures it doesn’t increase the overall cost.
- Choosing a technology stack that resonates with the software development process facilitates a flexible, supportive environment.
- Security is part of the software development culture to safeguard your product from cyber threats.
- Devising new problem-solving logic based on open-ended programming and supporting high-performance systems.
- Offering adequate education and training opportunities that team members need to work efficiently.
- Enabling software development process automation ensures developers spend less time on mundane tasks.