Summary: Web 3.0 is here, and experts proclaim it as a pivotal shift from the internet we know today. Businesses and leaders are exploring the potential of what could transform the digital landscape with the ‘read/write/own’ web shift. As the foundation of the present-day Web dynamics changes, let’s look at what Web 3.0 is, why it matters, and how it could shape the future of your business. Read on to explore and understand more.
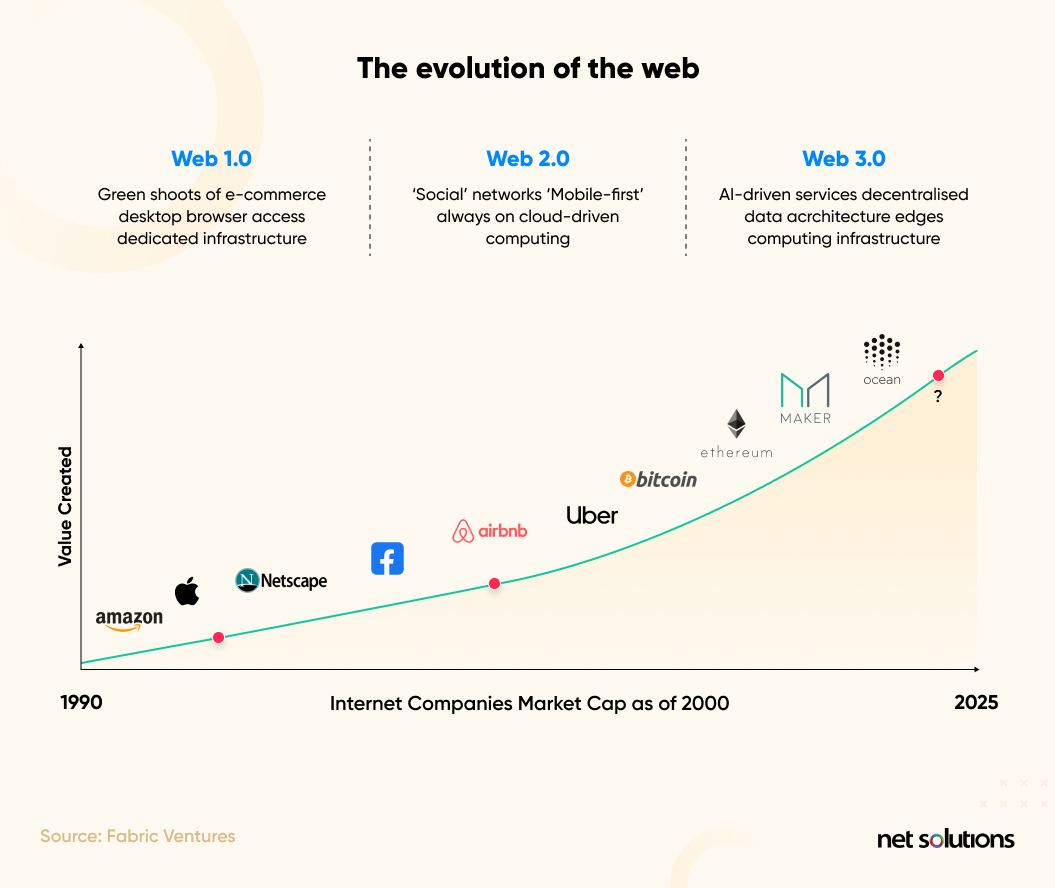
The early 2000s were the darkest years in the history of the Internet. Many online companies went out of business, and many others lost a significant portion of their market capitalization. For example, Cisco was an $80.06 stock in March 2000 but was reduced to only $8.6 by October 2002. The media, too, at that time, talked only about the Internet being a passing craze.
Only 48% of dot com companies survived the disaster, and these were those that didn’t give up and saw an opportunity in the crisis. Today, the same organizations rule the world and control a significant portion of the Internet. Google, Amazon, and Microsoft are prominent examples.
A similar narrative ran around Web 3.0 last year. While some called Web 3.0 the future of the Internet, others felt quite the opposite, as these tweets from Elon Musk and Jack Dorsey indicate.
So, what is Web 3.0, and why is there so much fuss around it? Is it just a fad or a next step into the evolution of the Internet? If it’s the next phase of the Internet, how can your business benefit from it? Read on to find out:
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the Internet. It is secure, decentralized, and free from the control of the Internet and social media organizations. This version of the Internet is based on blockchain technology and operates on token-based economics.
The idea behind Web 3.0 is to create an internet that accurately interprets your input, understands what you convey, and allows complete control over what type of content you want to consume.
An Overview of Web 3.0 Stack
Shifting from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 has minimal impact on end-users but involves radical changes at the backend. The technology stack for Web 3.0 will be different.
Here’s what it would look like:
1. Network Layer
The network layer is the lowest in the Web 3.0 stack. Contrary to Web 2.0, which relies on centralized databases, Web 3.0 will be powered by blockchain for trustless and permissionless access.
To choose a blockchain network for building decentralized applications (dApps), developers will have two options:
A. Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) Blockchain
An Ethereum blockchain-powered virtual machine stores critical information like accounts, balances, and machine states.
EVM Blockchain Examples
- Ethereum – Original EVM intelligent contract platform
- Polygon – Ethereum sidechain
- Arbitron – Layer 2 blockchain using Optimistic rollups and multi-round fraud proofs
- Optimism – Layer 2 blockchain using Optimistic rollups and single-round fraud proofs
- Hermez – ZK rollup Ethereum Layer 2 network managed by Polygon
- ZKSync – ZK rollup Ethereum Layer 2 network using SNARKs
- Starknet – ZK rollup Ethereum Layer 2 network using STARKs
- Avalanche – EVM-compatible Layer 1
- Cronos – EVM-compatible Layer 1
B. Non-EVM Blockchains
These blockchains don’t follow the Ethereum framework and are created by engineers who feel that EVM chains are too limited by the Ethereum framework.
Non-EVM Blockchain Examples
- Flow – Layer 1 using Cadence, Flow’s native resource-oriented programming language
- NEAR – Layer 1 using Rust or Assembly Script for intelligent contracts
- Solana – Layer 1 using Rust C and C++ for smart contracts
- Terra – Layer 1 using Rust for smart contracts
2. Blockchain Interaction Layer
The blockchain interaction layer allows developers and users to read and write data to the blockchain. Data providers, like block explorers, are a vital part of this layer. They serve as an online resource for retrieving real-time and historical data about transactions, address balances, gas fees, etc. Thus, the public can easily read and interpret blockchains.
3. Presentation Layer
This layer of the Web 3.0 stack contains high-level abstractions and frontend libraries, and it mirrors many aspects of Web 2.0 development.
4. Application Layer
The application layer contains customer interfaces for accessing Web 3.0. It ranges across Defi, NFTs, Identity & Authentication, Data & Analytics, and many other exciting dApp categories. The public consumers will interact with this layer to access Web 3.0.
Besides these four layers, Web 3.0 uses InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), a peer-to-peer hypermedia protocol. It makes storing and sharing files on the distributed web easy by using content-addressing to uniquely identify each file in a global namespace connecting all computing devices. Experts proclaim it as the future of internet protocols.
It is the Web 3.0 technology stack as of now. As the technology grows, we’ll see more infrastructure tools and paradigm shifts. While the stack will change, these Web 3.0 layers will stay.
Web 2.0 vs. Web 3.0: What’s the Difference?
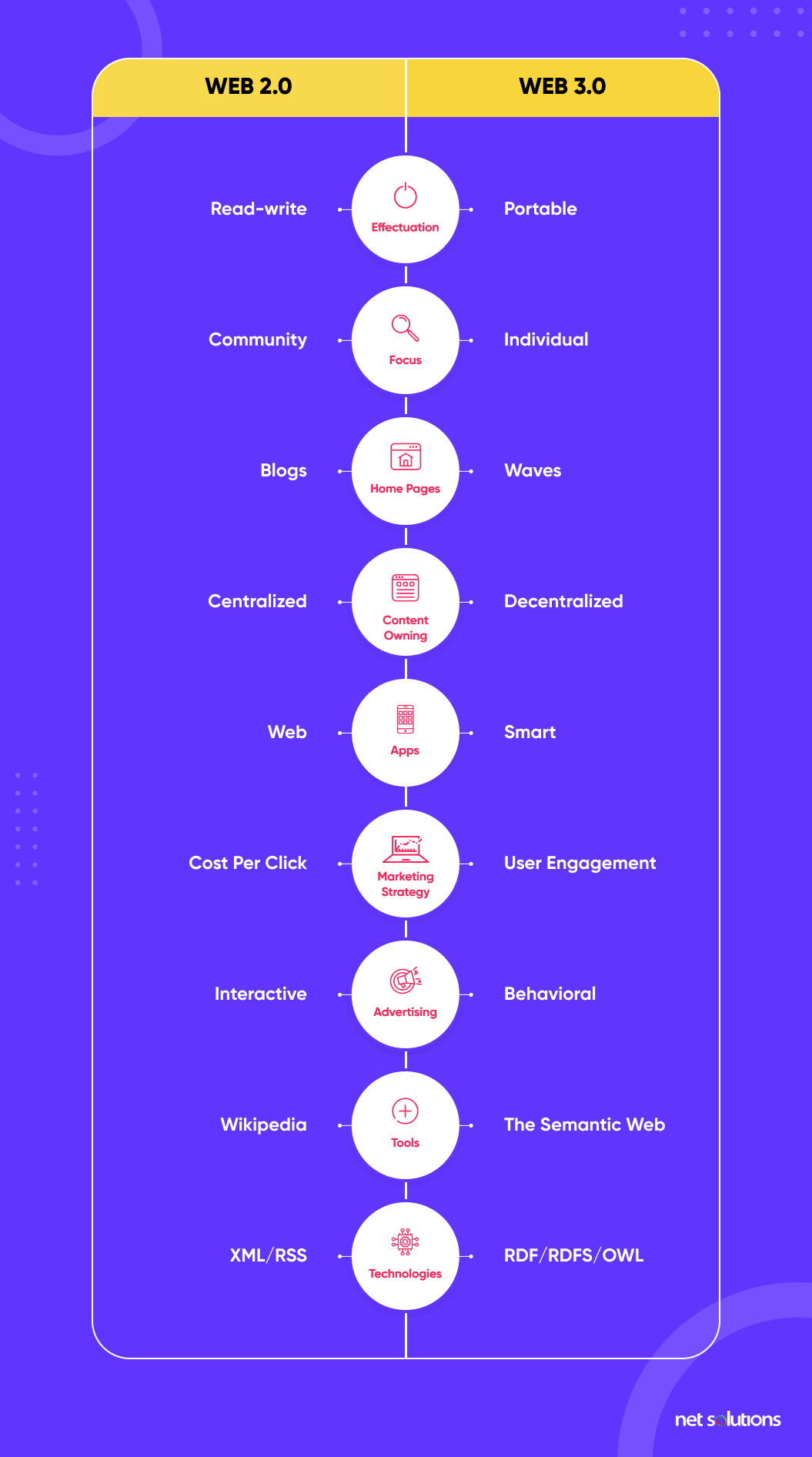
While Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 have a similar origin, both intend to solve the same purpose, i.e., offering the best experience to anyone accessing the Internet. Web 2.0 focuses on reading and writing content. On the other hand, Web 3.0 focuses on the essence. However, these two differences are just the tip of the iceberg. As you dig further, there’s a lot more:
| Focus | Web 2.0 primarily focuses on community development. | Empowering individual users is the primary focus of Web 3.0. |
| Content Presentation | Web 2.0 uses cookies to track users and offer personalized experiences. | Web 3.0 uses NFTs to assign value and offer some kind of perks. |
| Content Ownership | Data is owned and controlled by centralized authorities who use it the way they want. | Data is owned and controlled by the individual who created it. |
| Technologies | CSS3, HTML5, Ajax, and JavaScript are prominent technologies in Web 2.0. | Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and decentralized protocols will rule Web 3.0. |
| Types of Applications | Podcast, video streaming, communication, and content creation platforms are prominent in Web 2.0. | Web 3.0 will have a majority of AI and ML-powered apps (dApps) such as 3D portals, integrated games, and multi-user virtual environments. |
Real-life Examples of Web 3.0
The applications of Web 3.0 are yet limited. Still, we do see some websites and apps leveraging this technology. Here are a few examples of Web 3.0:
1. Social Networks
- Sapien: Sapien is a social news platform based on the Ethereum blockchain. It’s highly customizable and is an excellent alternative to traditional media like Google and Facebook.
- Steemit: A decentralized platform based on the Steem blockchain helps contributors monetize their content. It can be a great alternative to Reddit.
- Sola: A social platform that uses blockchain AI to ensure readers get helpful information according to their preferences.
2. Exchange Services
- IDEX: A popular decentralized exchange for trading ERC-20 tokens. Anyone with Ethereum Wallet can start trading on the platform.
- EOSFinex: A decentralized exchange running on EOS.IO software. The platform is in development by BitFinex, one of the largest exchanges.
3. Messaging Apps
- E-chat: A decentralized, secure messenger powered by blockchain technology. Not only can you enjoy secure chats with it, but they can also send Cryptocurrency through it.
- Obsidian: Obsidian is a next-gen messenger based on STRAT and powered by Stratis coin. It offers a secure environment where users can talk and send funds to each other.
4. Decentralized Data Storage Solutions
- Storj: A leading decentralized data storage solution where anyone can store data with just one click. It is fueled with Storj tokens.
- Sia: A promising decentralized storage solution splits a file into thirty segments and distributes it accordingly. Sia is the biggest competition to Storj.
5. Insurance & Banking
- Everledger: A distributed global registry that intends to create unique records for each user where they can digitally store data and access it anytime. It can be a great way to prevent yourself from fraud.
- Cashaa: This next-gen banking platform offers regulation, security, and compliance. You can even take crypto banking loans or engage in crypto trading.
6. Media Streaming
- LivePeer: A decentralized platform powered by blockchain that offers an open-source streaming service.
- LBRY: A decentralized digital library that houses different forms of content users can read, watch, and play on the platform. The platform supports books, music, and videos.
- UjoMusic: A music platform where creators can upload and distribute their music without worrying about copyright and royalty. Cryptocurrency and intelligent contracts power the platform.
- Maestro: A blockchain-powered music streaming platform for active listeners.
7. Remote Working
- Ethlance: Ethlance is a decentralized, remote working platform powered by the Ethereum blockchain. Here, anyone can hire or work in exchange for Ethereum coins. The platform has zero service fees or no membership restrictions of any kind.
- Atlas.Work: A blockchain-powered freelancing platform that uses smart contracts and machine learning to fuel a freelancing ecosystem where freelancers and hirers can reap maximum benefits.
- CryptoTask: CryptoTask is a blockchain-powered platform that uses advanced algorithms to help freelancers find the best gigs.
8. Web Browsers
- Brave: A fast privacy-oriented web browser that uses a blockchain-based digital advertising platform to redefine the web for users.
- Breaker Browser: A peer-to-peer web browser where everyone can join and share their apps.
Benefits of Web 3.0 for Businesses
1. End to the Monopoly of Tech Giants
Only a handful of organizations own and control the user-generated data. Not only do they exploit it at their will, but they also sell it to third-party service providers to earn revenue and influence user behavior.
Web 3.0 will end the data monopoly and centralized platforms that control users’ data. Decentralization will take center stage, and the complete data control will be in users’ hands. They will have the power to decide what data they want to share with businesses and earn money.
Even better, single centralized entities will not control Web 3.0, and the Internet will be a place owned and shared by everyone.
2. Fewer Intermediaries
In Web 2.0, many third parties are involved, between customers and companies. When customers purchase a product or service from a company, revenue gets shared with these intermediaries.
Web 3.0 directly connects companies with customers. No longer do they have to share their earnings with third parties. The need for monitoring transactions for fairness will still be there, but such authorities will be few.
3. Increased Security & Privacy
Website Security is the biggest issue for businesses in Web 2.0. Now and then, we hear of websites getting hacked and users’ data getting stolen. These incidents often cost millions, and let’s not forget the damage they cause to their reputation.
Web 3.0 will put an end to such instances. Data breaches and privacy hacks will become minimal, with privacy and security getting priority. Also, since Web 3.0 is decentralized, it will be impossible for hackers to breach the network without being traced.
4. Streamlined Business Operations
In Web 2.0, businesses spend most of their time streamlining their operations, which takes a massive chunk of their time and effort.
With Web 3.0, businesses can create and manage processes without much effort. With smart contracts, they can easily maintain a transaction ledger for everyone involved. For example, run a hotel business. You can access real-time information about guests, invoices, and bookings and offer personalized services to each guest based on their previous purchases and preferences.
5. Higher Transparency
One of the significant drawbacks of Web 2.0 is that it lacks transparency. Users hardly know what organizations do with their data. Although each organization lists its terms and conditions on its website, they’re so complex that they all barely understand them. It often leads to a lack of trust between businesses and customers.
Web 3.0 is a massive step towards ensuring transparency. Businesses can maintain transparency by sustaining an unchangeable record of transactions on the blockchain and making it visible to everyone. They can also become more accountable as it is possible to track each transaction.
Here’s how this will help:
- Users will have to spend less time researching products or services.
- There will be less involvement of third parties and increased trust as everything will be in front of their eyes.
Web 3.0 Challenges that Businesses Might Face
- Web 3.0 will put great pressure on businesses to modernize. They will be forced to modernize and enhance their websites to ensure they don’t lose their captured market.
- As Web 3.0 is relatively new, it will be a learning curve for companies engaged in web development services. They will need time and practice to get the hang of the technology.
- The decentralized nature of Web 3 will make it difficult to monitor and regulate it. Strong privacy policies will be needed to avoid the misuse of data.
How can Your Business Invest in Web 3.0?
Every technological revolution brings some fresh opportunities. Web 1.0 paved the way for companies like Amazon and Google, who saw an opportunity in online services. Web 2.0 cleared a path for companies like Facebook and TikTok that revolutionized the way people interact with each other.
Now, you might wonder What opportunities does Web 3.0 bring onboard? How can my business be a part of the Web 3.0 moment? If so, this section is for you. Here’s how your business can invest in Web 3.0:
1. Social Media
We already have social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn. However, they are all censored and controlled by centralized organizations, limiting the freedom of expression.
That’s when Web 3.0 offers an opportunity to build something that takes control from centralized organizations and brings it back to end-users. You can create a decentralized platform where no one can spin the narrative or misuse data – and everyone has the freedom of saying what they feel.
2. Currency Exchange Services
Existing currency exchange services are not safe from cyber threats. As we saw in the Mt Gox hack, around $460 million worth of bitcoins were hacked. Hence, it is crucial to create a decentralized currency exchange service where people can trade without worrying about cybercriminals. With Web 3.0, you can build such a platform.
3. Messaging Platforms
The Internet is full of adverse reports about the existing messaging platforms. They have highlighted two major issues that these apps suffer from.
- Unsafe transmission of messages.
- Reliability of centralized solutions prone to hacking and data misuse.
You can create messaging apps like YSign or Obsidian that operate on blockchain technology to maintain privacy and security. By giving people such a messaging platform, you can build an app that becomes popular on an even grander scale than WhatsApp or Telegram.
4. Data Storage Solutions
Most data storage services we use today, like Google Drive and OneDrive, are centralized. It means the organization managing it has control over this data. They can use it however they want or sell it to third-party advertisers. Sometimes, these storage solutions can be breached and fall into the wrong hands.
You can leverage Web 3.0 to build decentralized data storage solutions. You can create a platform that first encrypts the data and shares it through a peer-to-peer network. As a result, the data will not be stored in one place but on multiple nodes – making it foolproof against manipulations and cyber attacks.
5. Streaming Services
We have platforms like Netflix and Spotify that rule the media streaming space. However, they are often accused of misusing the audience data for advertisement purposes and not paying creators enough. Then, there are copyright issues that tarnish the reputation of these platforms.
By leveraging the Web 3.0 technologies, you can build a decentralized platform that leverages smart contracts to ensure transparency with creators and content consumers. Also, there will be no copyright issues because of these contracts.
6. Web Browsers
Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox currently rule the Web 2.0 space. However, we often hear reports of security breaches and data misuse.
It leads to the need for the next generation of web browsers powered with Web 3.0 and can protect users’ data without misusing it or even earn some bucks if they share their data with you. By building such web browsers, you can create something that offers users a better alternative than existing options.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does Web 3.0 already exist?
While Web 2.0 dominates the Internet, some aspects of Web 3.0, such as Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology, already exist. Web browsers like Brave and social networking sites like Sola offer decentralized experiences to customers with artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. As we progress further, we’ll see more of Web 3.0.
2. How is Web 3.0 changing the world?
Driven by Blockchain technology and operating on a revolutionary new model called decentralization, Web 3.0 is making the world a better place by eliminating intermediaries, manual mediation, and arbitration, reducing costs. It is paving the way for the Internet that’s equal for everyone and free from the clutches of centralized organizations.
We’re not far from the day when the monopoly of the tech behemoths will end, the established brands will undergo a significant overhaul to survive the change, and businesses will have to look for new ways to conduct their business.
3. What is Web 3.0 also known as?
Web 3.0 is also known as the semantic web, making it possible to edit information so that machines can process it.
4. Will Web 3.0 replace Web 2.0?
While Web 3.0 will not entirely replace Web 2.0. It will pave the way for new opportunities and open a new frontier of web development based on AI, IoT, and blockchain technology.
5. What are Decentralized Web Apps in Web 3.0?
Decentralized web apps (or Web 3.0 Blockchain apps) are apps powered by blockchain technology. They intend to make the web open and transparent and bring the power of data back to the end-users.
Is your current tech stack ready for the future?
Talk to our experts to deliver on tomorrow’s customer needs


 Updated: July 1, 2022
Updated: July 1, 2022