Choosing your product depends on your budget, requirements, suitability, and deadline. In software development, testing determines if the software product meets the expected requirements and is free of defects. This process is completed using manual or automated tools. Let’s understand automation testing in detail.
The importance of proactive and continuous software testing cannot be underestimated; helping find and fix bugs early in the development process saves both time and money, allowing bugs to be fixed before they become “baked in.”
Further, the process helps speed time-to-market, an essential process with changing market pressures and customer demands. Developers leverage automation to get the most out of continuous software testing and speed up time-to-market.
In this guide, learn more about what automation testing is and why it is used when it is most appropriate (what kinds of tests to automate), the top test automation tools, how to choose among them, and the best practices for it.
The Fundamentals of Automation Testing
What is automation testing?
Automation testing (automated software testing or test automation) uses an independent software tool to execute tests, comparing actual outcomes against predicted outcomes. Automation aims to increase efficiency, reduce cost, and improve the quality and security of the software being tested.
Automation testing has been critical for software development for many years. Still, in the past few years, the proliferation of open-source and low-cost tools has made it more accessible for more organizations and projects.

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
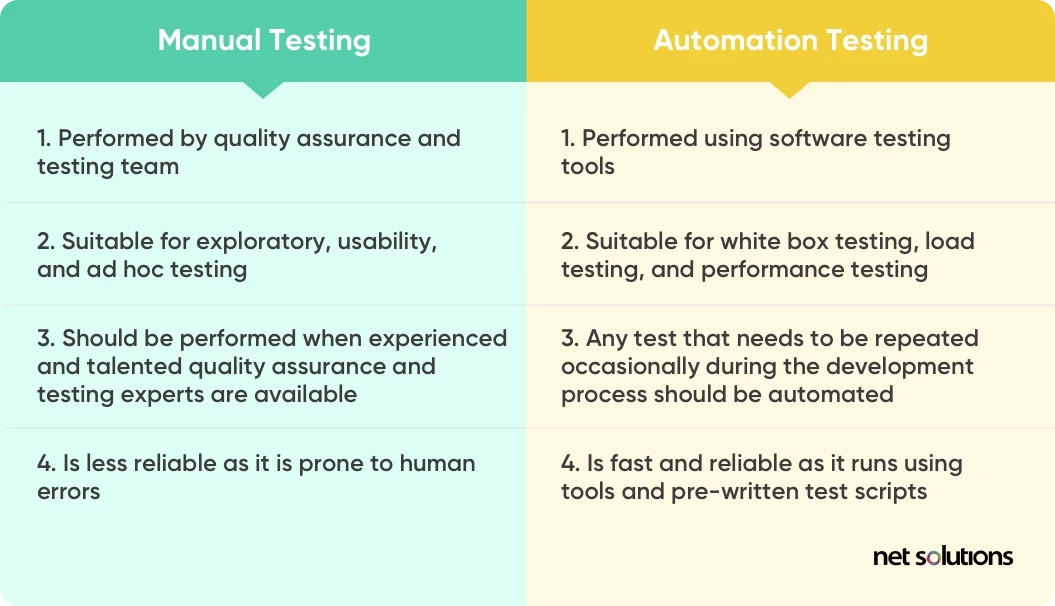
Benefits of automation testing over manual testing
In manual software testing, the developers or test engineers check the software’s features, uses, and functionalities against the test cases without assistance from available tools and software. Manual testing can be time-consuming, prone to human error, and difficult to scale as the software becomes more complex.
In automated testing, developers use specialized tools to automate and control test cases, with test cases executing automatically without any need for human involvement after the test case is prepared. Automated testing is ideal for large or complex software that requires continuous or repeated testing of pre-written scripts. Automated tests can be run simultaneously across different components or platforms, making it well suited for Agile development and its focus on iterative, continuous testing to find and repair bugs early, speeding up development.
While it may seem like automation testing is only the replacement of manual testing with automation tools, there are key differences that make it more reliable than manual testing
- Automation testing helps increase the number of tests that can be run concurrently
- It can increase the depth/scope of the tests being run
- You can scale Automation testing without extra work
- Manual, human testing is prone to human error – but automation testing is not
- It can leverage simulated user groups of any size
- Automation testing can initiate automatically whenever source code changes, reducing the ask of developers
- Burnout associated with repetitive tasks is eliminated by automation testing
The differences are more clearly understood as under:
Most software is developed using a combination of manual and automated software testing, depending on the use case. For example, if a test is only run once or twice, it is unsuitable for automation. It is up to the assurance and testing team to determine which testing they prefer for each stage of the development process.
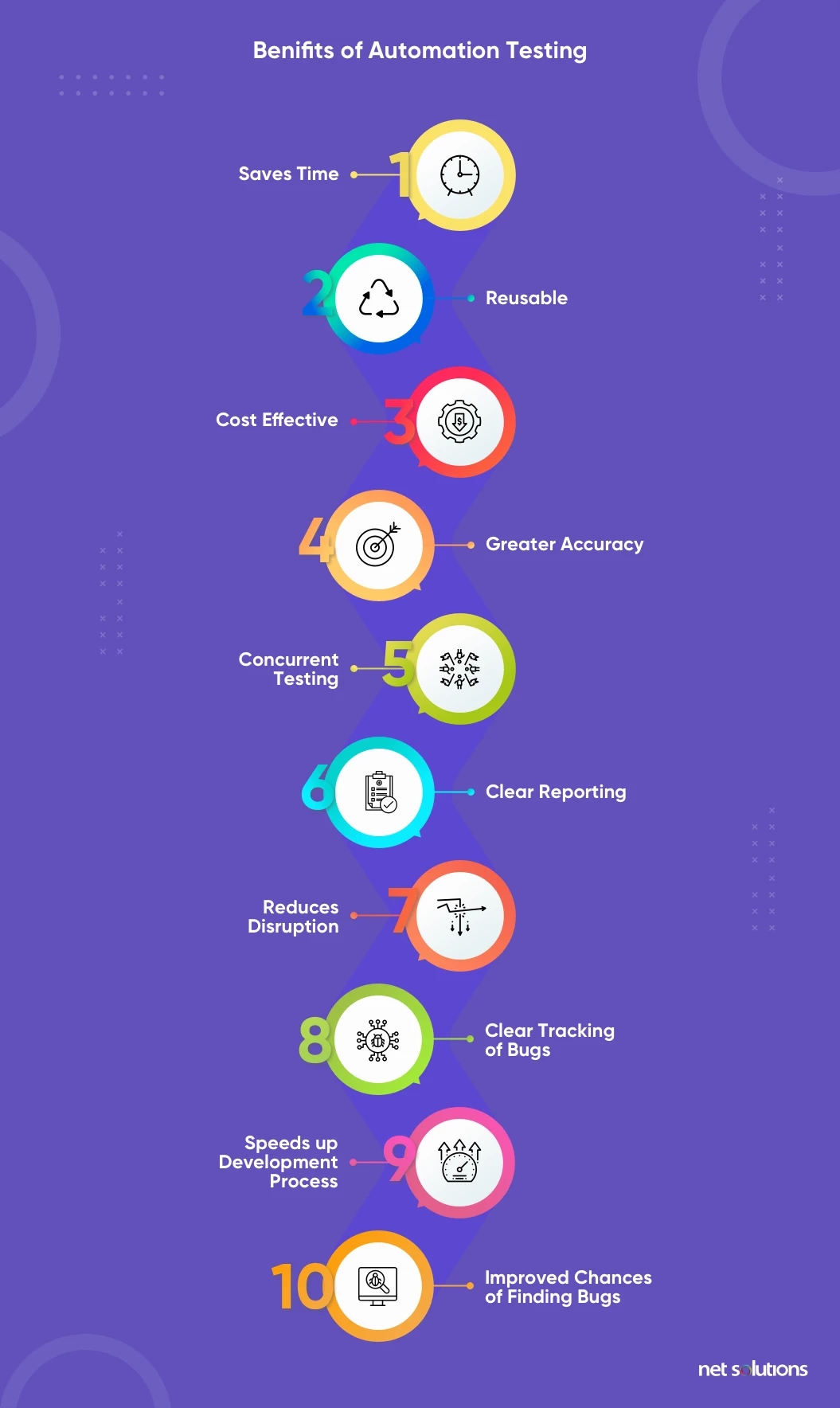
Some of the benefits of automation testing include the following:
- Saves time
- Reusable
- Cost-effective
- Greater accuracy
- Concurrent testing
- Clear reporting
- Reduces disruption
- Clear tracking of bugs
- Speeds up the development process
- Improved chances of finding bugs
Types of Automation Testing
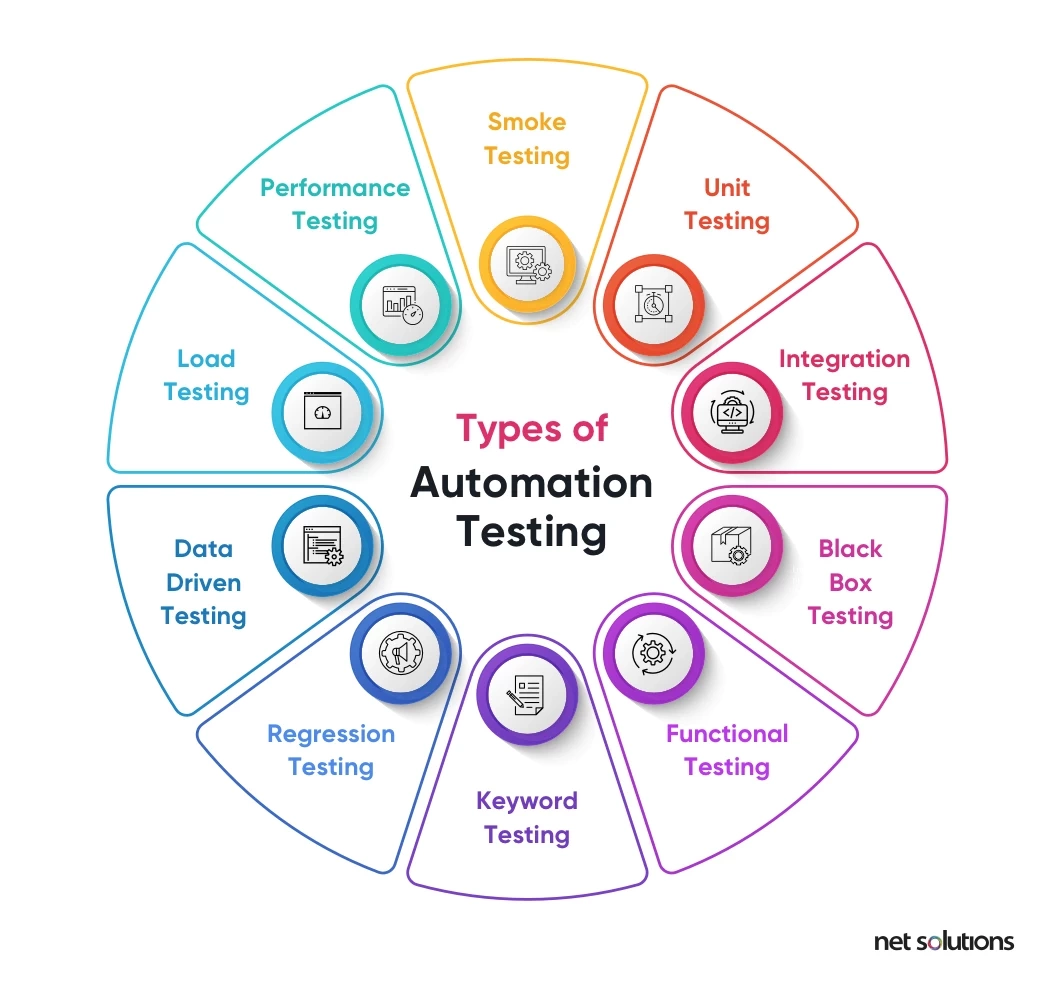
Not all types of software testing are best suited for test automation. The best kinds of tests to automate are –
1. Smoke testing
Smoke testing is the initial software testing to identify the fundamental problems that could restrict the software from running.
2. Unit testing
A unit test helps identify bugs in a single module of the code. In Agile development, unit testing will identify the bugs in a single user story developed during a time-boxed sprint cycle.
3. Integration testing
Integration testing helps test the integrated version of the software for its wholeness, i.e., when two or more modules are clubbed together.
4. Black box testing
Black box testing assesses specific functions or features of the software without going into its inner workings.
5. Functional testing
Functional testing is a quality assurance process and type of black-box testing that looks at the most critical aspects of the software.
6. Keyword testing
Keyword testing (keyword-driven testing, action word-based testing) is a type of functional testing that uses familiar action words to represent user behaviors (design of the test), documented separately from the actions (the development of the test) and its execution.
7. Regression testing
If a significant change is made to a part of the software, regression testing runs the test cases to ensure the software performs as expected.
8. Data-Driven testing
Data-driven testing (table-driven or parameterized testing) stores test data in a table/spreadsheet, with a single test script able to execute all test data and return the results in the same table.
9. Load testing
A load test helps determine the efficiency of software under stress conditions, i.e., if there is an increase in the number of users or when it is handling a significant spike in traffic.
10. Performance testing
Performance tests are conducted to test the software product’s speed, responsiveness, intuitiveness, and stability. In Agile Testing, performance testing can be checked at the end of each sprint that delivers a user story. This ensures a good testing speed and timely delivery of high-performing products or fragments of the product.
11. Security testing
You can also automate security testing to validate all user input, reducing the chances of cyberattacks like command injection, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Test Automation vs. Automation Testing
Test automation and automation testing are related concepts in software development and quality assurance. While they are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference between them.
Test automation refers to using software tools and scripts to execute tests and compare the actual results with the expected outcomes. It involves automating the repetitive and time-consuming tasks of running tests, allowing for faster and more efficient testing.
Test automation is typically used to automate functional, regression, and performance tests. It aims to improve the speed and accuracy of testing, reduce human errors, and enable quicker feedback on the quality of the software under test.
On the other hand, automation testing is a broader term encompassing the entire process of using automation tools and techniques to perform various testing activities. It includes not only test execution but also test data generation, test environment setup, test result analysis, and reporting.
Automation testing involves designing and implementing automated test suites covering many cases and scenarios. It focuses on streamlining the testing process by leveraging automation to reduce manual effort and increase testing coverage.
Frameworks for Automation Testing
Data-driven automation framework
This framework allows testers to separate test data from test scripts, enabling the reuse of test scripts with different data sets and efficiently executing many test cases.
Keyword-driven automation framework
Testers define keywords or action words representing specific test steps with this framework. Test scripts are created using these keywords, making test case maintenance and readability easier, even for non-technical team members.
Modular automation framework
The modular framework divides the entire application under test into modules or components. Each module has its test script, making it easy to maintain and update test cases independently, promoting reusability and scalability.
Hybrid automation framework
The hybrid framework combines multiple frameworks, such as data-driven and keyword-driven, to leverage their advantages. It allows for flexibility and accommodates varying testing needs, balancing the reusability and maintainability of test cases.
Top 10 Automation Testing Tools
There are more automation tools than test cases, making knowing what to choose or when difficult. While the next section will help select the right automation tool, the top 10 automation testing tools are:
1. Selenium
An open-source testing tool for web application testing across multiple programming languages, OS, and browsers. Currently ranks #1 for web app testing.
2. Appium
Open-source testing for hybrid or native iOS / Android mobile apps.
3. Katalon Studio
Testing for web, API, and mobile app development with a simplified keyword tool for creating test cases. Works on top of Selenium and Appium and integrates with various other tools.
4. Cucumber
Open-source behavior-driven development (BDD) tool for web development/user experience. The test code is written in Gherkin (simple English).
5. HPE Unified Functional Testing (UFT),
Formerly known as QuickTest Professional (QTP), it is a cross-platform automation tool for functional and regression testing for software applications and environments and offering keyword and scripting interfaces.
6. WorkSoft
Testing for SAP, the only code-free continuous test automation platform.
7. IBM Rational Functional Tester (RFT)
Commercial testing tool for automated functional and regression, GUI, and data-driven testing.
8. Telerik Test Studio
Windows-based testing tool for web and desktop functional, performance, load testing, and mobile app testing.
9. SoapUI
An open-source functional testing tool with a comprehensive API test automation framework for Representational State Transfers (REST) and Service-Oriented Architectures (SOAP).
10. TestComplete
Functional test automation tool for desktop, mobile, and web apps that includes keyword-driven, data-driven, regression, and distributed testing. Known for recording & replay functional UI tests.
Related Article: Insight into the Top 10 Automation Testing Tools for 2022
5-Step Automated Testing Process
The following outlines how to set up automated testing:
1. Define the scope of automation
Define the requirements of the test to determine if it is a candidate for automation. Next, define what the test case is supposed to do.
2. Evaluate and select tools
Choose the right tool for the test (as discussed in the above section).
3. Planning, design, and development
Design and develop the test cases. Start small to determine if the automation is effective. Clearly label and document test cases being automated.
4. Test execution
Run the first test to ensure it works correctly. Set up the test frequency (regular or triggered by other events).
5. Maintenance
Test cases must be reviewed and maintained as the software evolves to incorporate any changes that could cause tests to fail or become misleading. If this happens frequently, it may not have been the proper automated test.
Steps to Choose an Automation Tool
In determining a test automation strategy, a QA team will create a plan for testing that will outline the approach and goals of the project, including which tests will be automated and which not. Next, the team will weigh the pros and cons of various tools for automation testing.
An automation tool is about choosing the right one at the right time. The factors to be considered in making that choice include:
- Cost
- Support for the environment/technologies in use
- Supports multiple testing frameworks (if relevant)
- Supports the kind of testing that needs to be run
- Easy to use / training time
- Script development is easy
- Availability of tool experts (internal or outsourced)
- Strong reporting capabilities
- Availability of support (technical or community)
- Availability of recording
- CI/CD capabilities
- Integration with bug tracking or task management systems
Automation Testing Best Practices
When turning to automation, it is essential to automate the right test cases but also to set up automation to have the maximum return by following these best practices:
- Test only what is necessary and repeatable
- Use data-driven tests
- Test early and often
- Create tests resistant to frequent maintenance (particularly for UI)
- Ensure the test does not introduce new technical challenges
- Test on real devices (if relevant)
- Keep good records (well-structured)
- Ensure testing leads to action (tasks)
- Share the responsibility for testing
Limitations of Automated Testing
While there are many benefits to automation, there are limitations as well. As noted, automation testing is inappropriate for all scenarios, and much time can be wasted writing a test for a situation that is prone to change or that won’t be used frequently enough to warrant investment.
Further, automated testing needs to be data-driven, but not all feedback is quantitative. For example, automated testing is inappropriate for qualitative data, such as would be required to test the user experience.
Will Automation Testing Replace Manual Testers?
This is a common concern, but test automation – even test automation backed by artificial intelligence – CANNOT replace manual testing. Not all test cases or projects are suitable for test automation. And in some cases, automation lacks the nuance of the human brain to spot complex issues or opportunities for improvement that true professional QAs from any software testing company can spot.
4 Common Misconceptions About Automated Testing
The following are common myths and misconceptions about automated testing:
1. Every test can be automated
Fact: Not all tests can or should be automated. If the test is not done frequently enough, or if it won’t save time to automate it, it should not be automated. Most automated tests are done early in development for low, stable, fixed, or complex tests and are prone to human error.
2. Automated testing is expensive
Fact: While the initial cost to set up test cases for automated testing may be high, the long-term cost of reusing those test cases over and over reduces the overall time (and cost) spent testing. Further, many tools for automated testing are free and open-source.
3. Automation testing is better than manual testing
Fact: There is no better or worse in manual vs. automated testing; only the kind of testing is right for the job. Each approach is right for different situations and stages of the development process.
4. Test automation setup is a one-time-only event
Fact: Once you have set up a test, it will be used repeatedly in its current state. However, the test script must be updated to remain relevant if the environment changes.
Agile Testing is a holistic approach to “bake in quality” to the digital product, taking on the agile manifesto’s principles and values to speed up the testing process while ensuring collaboration among the testers and developers towards the common goal — quality software development. Software that’s developed quickly – but also quality and secure software.
How Can Net Solutions Help You?
With over 23 years of experience building custom eCommerce apps, Net Solutions has helped multiple platforms drive advancement. We have efficient and comprehensive automation testing processes that help boost the platform’s performance and help them grow foolproof – like we did with American Golf.
Net Solutions overhauled the platform via rigorous planning, innovative design, and faultless execution to offer expanded functionality, improved user experience, and higher client engagement. Because of their team’s technological expertise and customer-centric approach, American Golf was able to increase its online presence, extend its reach, and drive company development.
The important contributions of Net Solutions were critical in propelling American Golf’s platform to new heights of success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Low-code development platforms provide an alternative approach to traditional software development, enabling faster application development with minimal coding. While low-code platforms can facilitate certain aspects of test automation, such as creating test scripts or building test workflows, they do not replace the need for dedicated test automation tools and frameworks.
To start preparing for automation testing, follow these steps:
- Gain a solid understanding of manual testing principles and techniques.
- Learn programming languages commonly used in test automation, such as Java or Python.
- Familiarize yourself with popular test automation frameworks and tools like Selenium or Appium.
- Practice writing automation scripts and executing them against sample applications.
- Explore different types of test automation, such as functional, performance, or API testing.
- Keep up with industry trends and best practices through blogs, forums, and online courses.
- Collaborate with experienced automation testers or join communities to learn from their experiences.
The four stages of automation typically followed in a test automation process are:
- Planning: This stage involves identifying the scope of automation, selecting appropriate test cases for automation, defining goals, and establishing the automation strategy.
- Development: In this stage, automation frameworks and tools are selected and set up. Test scripts are created using programming languages and automation tools, and necessary test data and test environments are prepared.
- Execution: The automation scripts are executed against the application under test. Test results are logged, and any failures or issues are reported. This stage involves running automated tests and validating the expected outcomes.
- Maintenance: After executing the tests, any failures or issues are investigated and resolved. Test scripts may need to be updated to accommodate application or test requirements changes. Regular maintenance ensures the automation suite remains up-to-date and effective.
Agile test automation is integrating test automation into the Agile software development methodology. It emphasizes the need for quick feedback and continuous testing throughout the development lifecycle. Agile test automation focuses on creating and maintaining a suite of automated tests that can be executed repeatedly during Agile development iterations.