Whether you own a small-scale or a large-scale business, you look forward to reducing costs and maximizing profits. Cloud computing can help you achieve this goal by lowering upfront costs and letting you easily scale resources based on market demand, quickly respond to market needs, and automate tasks.
However, before switching your business to the cloud, you must understand the differences between cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS). It helps you decide on the right cloud strategy and ensure maximum success.
In this blog, we’ll clarify the confusion of IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS by comparing these three approaches in detail. We’ll discuss their differences, pros and cons, and which approach you must use depending on different situations. Let’s begin:
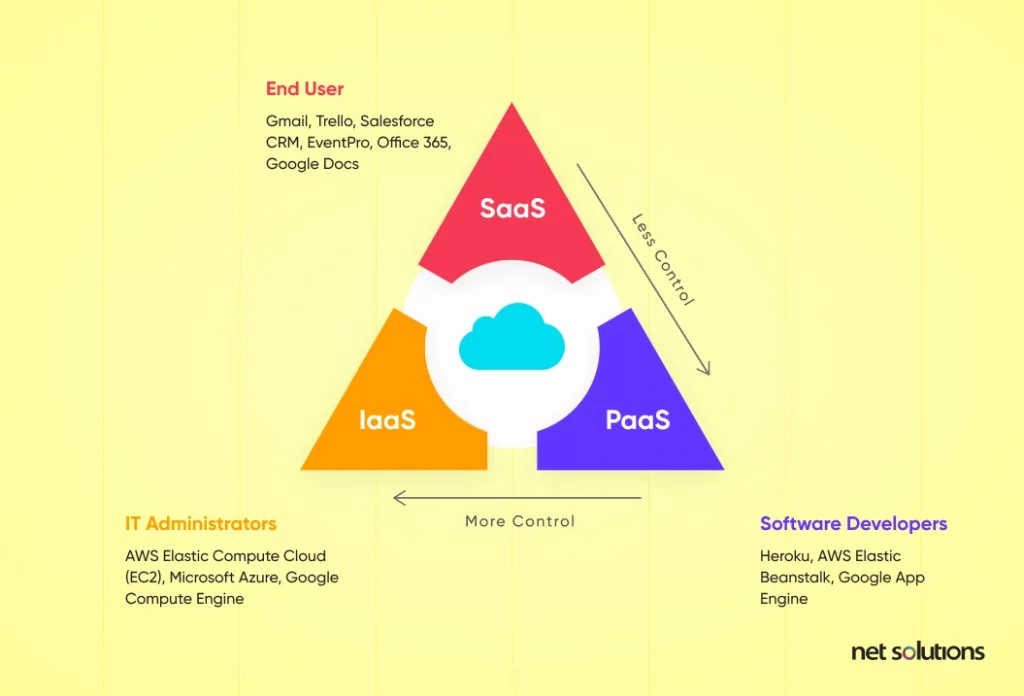
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the acronym for Infrastructure as a service that provides businesses a complete infrastructure, i.e., storage and server space to experiment and build new technologies over the cloud. IaaS services can host websites and software solutions, build virtual data centers for large-scale enterprises, and conduct data mining and analysis.
Here, a business is responsible for managing the application hosted, the particular development tools, and the operating system deployed. On the other hand, the IaaS vendor manages the storage space, networking resources, and the dedicated data center.
A perfect IaaS example is Amazon Web Services (AWS), leading the public cloud space. Big players such as Salesforce and Netflix already leverage AWS to support their ever-growing client/customer base.
Advantages of IaaS
- Cost-reduction: IaaS is the most affordable cloud computing strategy, with lower infrastructure costs. Organizations with IaaS don’t require worrying about network equipment or hardware maintenance. Starting with limited resources and experimenting with new ideas is an economical option for start-ups or new businesses.
- IaaS Keeps Running Irrespective of Any Challenge: Cloud providers spread resources across multiple servers and data centers in IaaS. It means your infrastructure keeps running even if a hardware component fails, one of the servers goes down, or an entire data center goes offline.
- Focused on Business Growth: While building your own company, worrying whether the data infrastructure can keep up with the organization’s growth can be daunting.
Since a third-party service operates the latest Infrastructure, the newest technology easily scales up and down according to businesses’ needs; thus, you don’t have to worry about technology updates. You can focus on other work as a third-party service that operates the Infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Modern work demands greater flexibility, so adopting IaaS provides flexibility as employees can access their records and data offsite. They can also connect to the virtual office easily and quickly.
Disadvantages of IaaS
- Security: While the cloud providers are responsible for infrastructure security in IaaS, the security of the applications, data, and the operating system you deploy on the IaaS is still your responsibility. Hence, it requires combined efforts from your and the cloud providers’ end. Any negligence from your or their end may make you prone to security breaches.
- Technical Issues: Businesses face some downtime with IaaS; thus, it restricts their access to applications and data.
- Over Dependency: Dependency on the provider, whose sole responsibility is ensuring the service is available and secure.
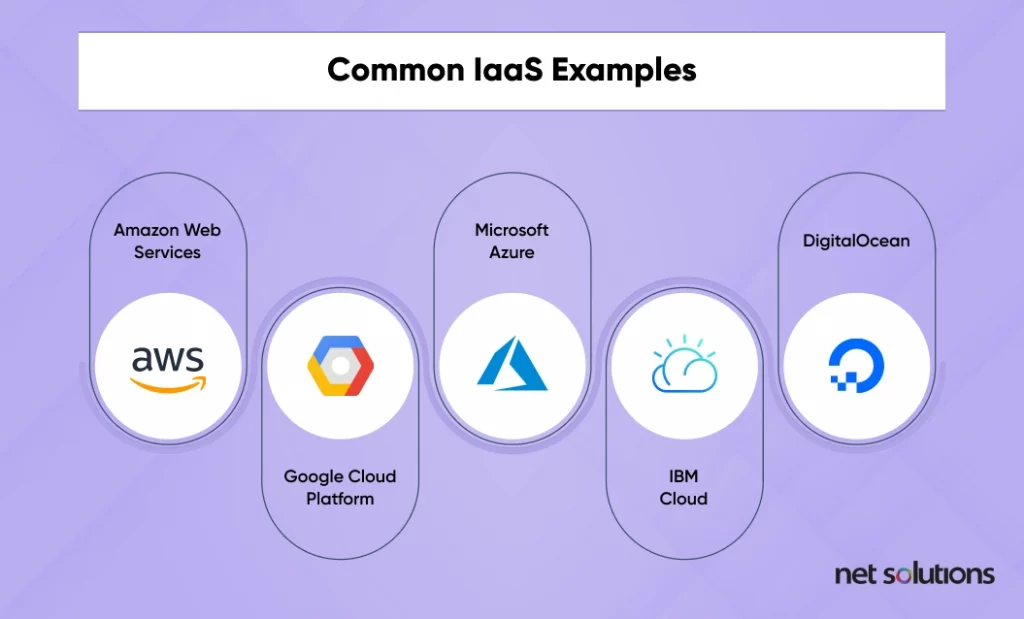
Common IaaS Examples
Here are a few common IaaS examples:
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
An acronym for the platform as a service, PaaS is a cloud strategy that offers a dedicated framework for developers to build, test, deploy, and manage new product applications.
A prominent example of PaaS is Google App Engine, which helps developers produce and host applications easily.
Advantages of PaaS
- Minimal Development: PaaS services allow rapid prototyping and development by providing prebuilt backend infrastructure and other resources. A platform offers access to tools, templates, and code libraries, reducing development time and simplifying the process.
- Cost Reduction: PaaS services are the most viable option for companies willing to reduce operating costs or develop an application for the first time with limited resources. It eliminates the need to build applications from scratch and reduces the costs associated with development.
- Flexibility: PaaS services allow employees to log in and work on applications from anywhere. It also provides the flexibility of being deployed across multiple channels and a range of connected devices.
- Future-Proof: With a PaaS platform, new features, capabilities, and bug fixes are instantiated automatically in the cloud. That way, the focus can be on core business initiatives rather than maintaining underlying IT infrastructure.
Disadvantages of PaaS
- Vendor Lock-in: Switching PaaS providers after building an application using specific tools and platforms can be hard. Each vendor may not support the same languages, APIs, or operating system that makes and runs the applications. Thus, it’s very much dependent on the PaaS providers.
- Security Concern: Security is a shared responsibility between you and the cloud provider in PaaS. While the PaaS provider secures the operating system and the physical infrastructure, securing the applications, data, and user access is still your responsibility. The downside of this approach is that the negligence from either your or the provider’s end can make you vulnerable to security threats.
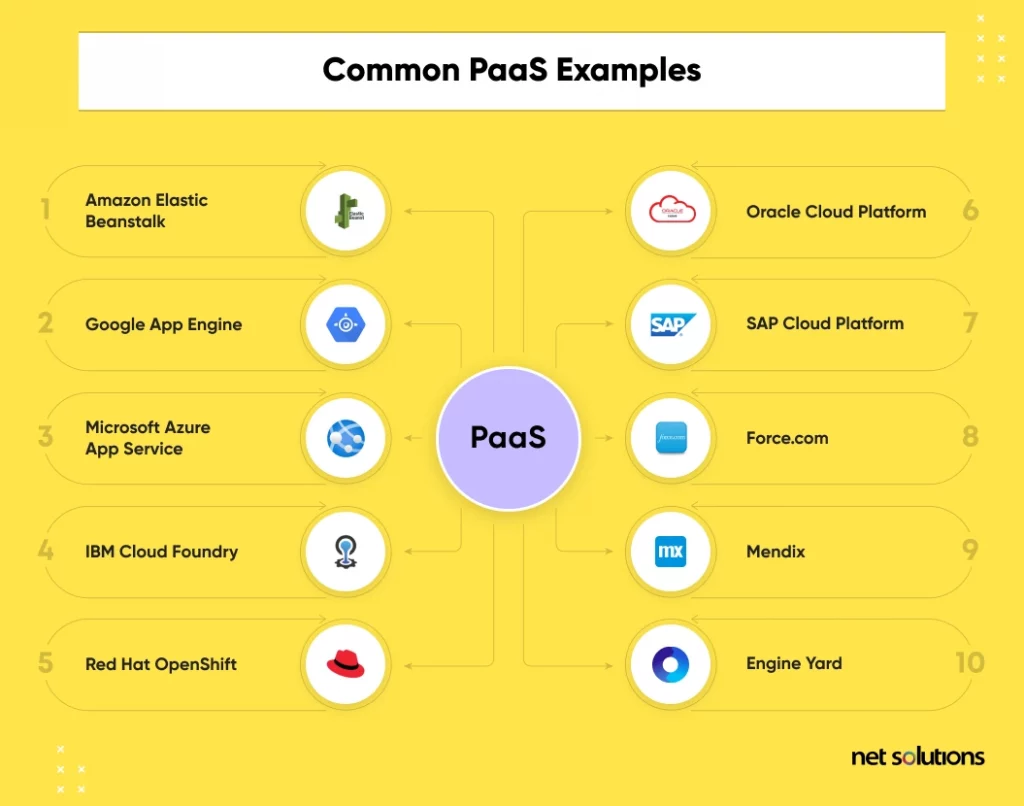
Common PaaS Examples
Here are a few common PaaS examples:
Software as a Service (SaaS)
An acronym for Software as a Service, SaaS is a cloud strategy in which we host the software centrally and license it on a subscription basis. Users can access SaaS applications over the internet via a web browser or mobile app.
One of the most relatable SaaS examples is Google Docs, which allows the creation and sharing of documents, and Dropbox, which enables file sharing and downloading over the network.
Advantages of SaaS
- Lower Costs: SaaS allows cost reduction with vendor-managed servers. Software as a service model offers flexible payment methods such as paying on an as-you-go basis (only paying for the services you use). It doesn’t require hardware or maintenance costs.
- Operational Management: SaaS applications are free from the burden of lengthy traditional software deployment delays since they are available on the cloud. They don’t need installation, equipment updates, or traditional licensing management.
- Scalability & Integration: A SaaS solution can be easily scaled to accommodate the changing business needs. Compared with the traditional model, one doesn’t have to buy another server or software.
- Accessibility: A browser and an internet connection are required for running a SaaS application, but they’re generally available on a wide range of devices and anywhere globally.
Disadvantages of SaaS
- Lack of control: Hosted cloud services offer lesser power as they reside with a third party than in-house software applications, which provide higher control.
- Stability: SaaS Applications require a good and stable internet connection. Hence, connectivity can be an issue, with a constant requirement for a stable internet connection to work efficiently.
- Security: Lack of transparency, security issues, and privacy of sensitive information are primary considerations around cloud and hosting services. These are some of the primary reasons some companies hesitate to use SaaS.
- Vendor Lock-in: Some SaaS vendors use proprietary data formats. As a result, migrating data to a different platform can be time-consuming and challenging. Also, not all providers offer the same integration support and customization options. All these factors lead to high switching costs, and consumers remain locked in with a vendor even if they’re charging them a higher fee than others.
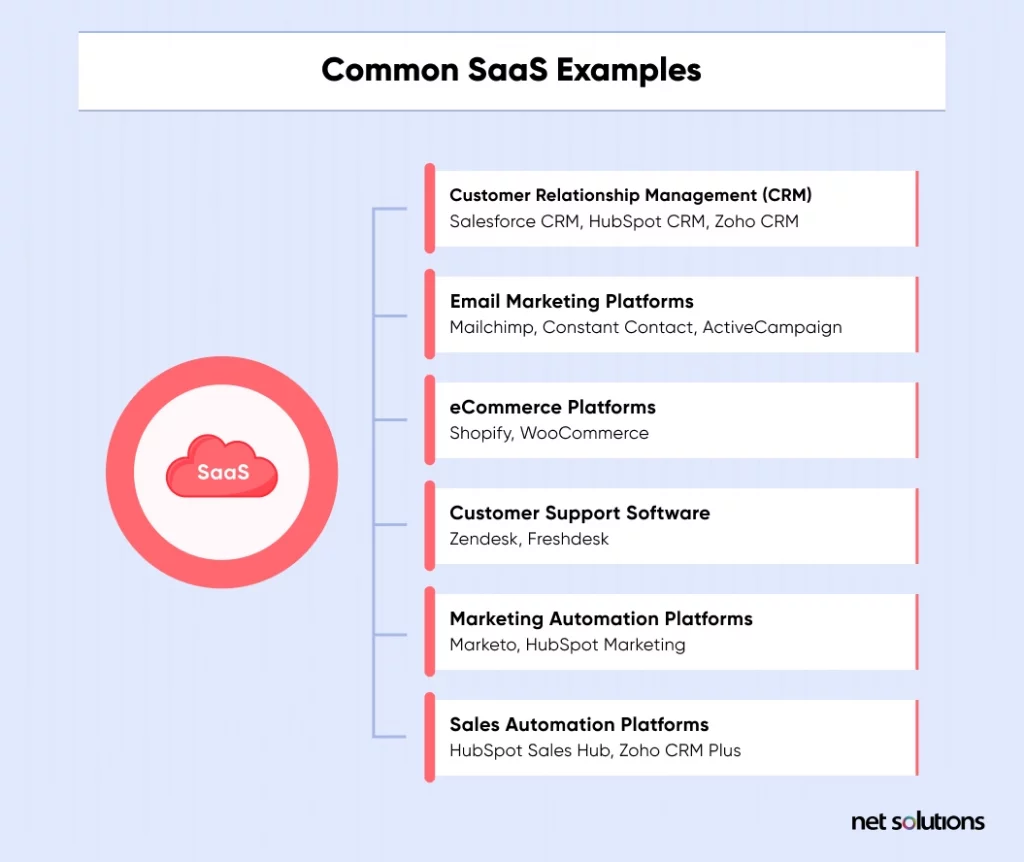
Common SaaS Examples
Here are a few common SaaS examples:
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: What’s the Difference?
Here’s an image explaining the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS:

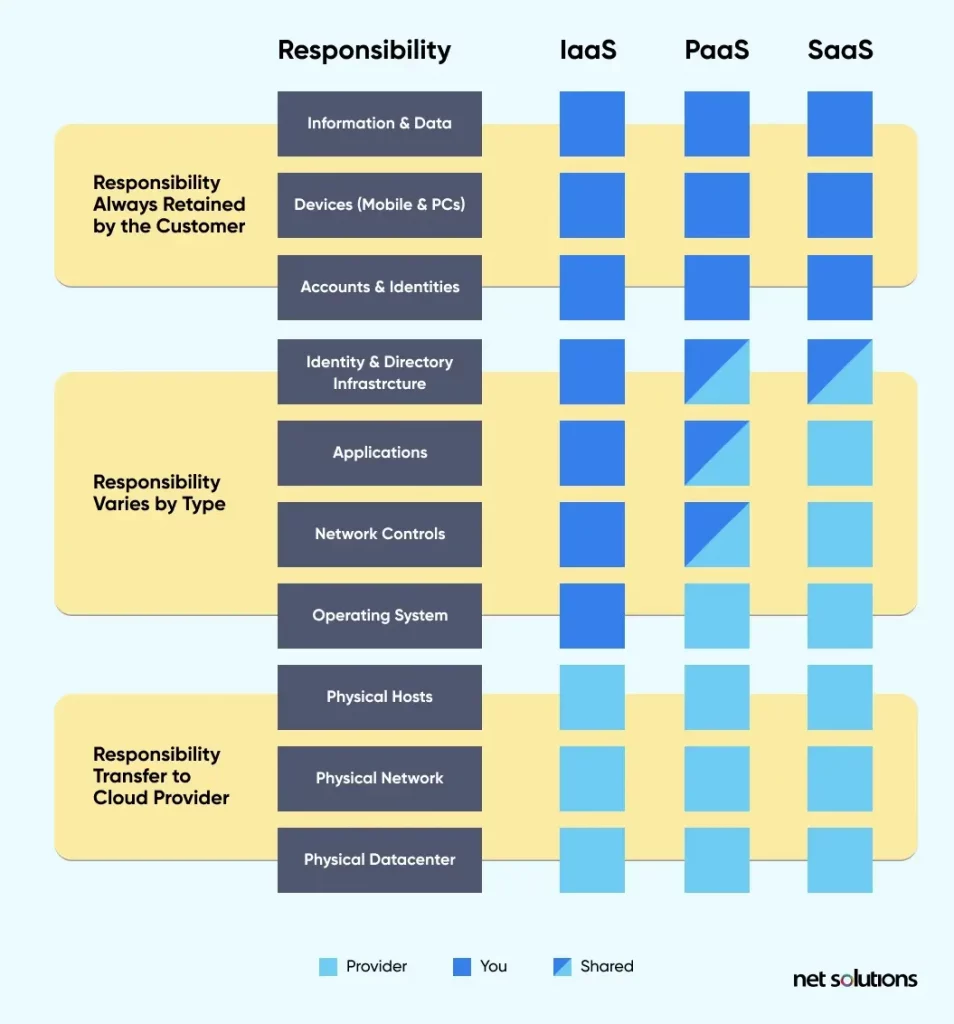
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Who Manages What?
When it comes to IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS, it is imperative to know what you manage vs what the vendor manages. Here’s an image explaining the division of responsibilities in each model:
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Which Cloud Strategy Should You Choose?
The best cloud strategy among IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS depends on your project requirements.
Here is a general overview of when each service model is most appropriate:
When to Choose IaaS?
You must choose IaaS if:
- You want a high degree of control over its infrastructure.
- You want to run custom applications unavailable as SaaS or PaaS applications.
- You need to integrate your cloud infrastructure with your existing on-premises infrastructure.
- When you have specific compliance requirements that you must meet at any cost.
When to Use PaaS?
You must choose PaaS if:
- You want to focus on developing and deploying applications without having to manage the underlying infrastructure.
- You need to develop and deploy applications quickly.
- You need to scale its applications up or down easily without any hassle.
- You want to reduce the cost of developing and deploying applications.
- You want to improve the reliability and security of your applications.
When to Use SaaS?
You must choose SaaS if:
- You need to use a ready-to-use software application quickly and easily.
- You need to scale your software usage up or down easily.
- You want to reduce the cost of using software applications.
- You want to improve the reliability and security of your software applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, you can combine different cloud computing models for different use cases. The approach is known as a hybrid cloud or multi-cloud strategy. We combine public and private clouds in a hybrid cloud, while a multi-cloud strategy combines two or more public clouds.
Different cloud computing service models impact your business’s scalability and performance:
- SaaS is easy to start. But you depend completely on the cloud service provider for scalability and performance.
- You can easily scale your applications on PaaS, but you must depend on the cloud service provider for performance.
- IaaS offers the maximum scalability and performance. However, you’re responsible for managing everything.