Summary: Building a SaaS business is not enough. You also need a Saas business model to figure out how to make money from it. Read on to learn everything there is to building a Saas business model, why it matters, and how to implement this model in your online business.
The last two years were golden for the software (SaaS) industry. Many new SaaS startups emerged while many became unicorns. Not only did we see Zoom boosting its revenue by almost 600%, but remote and hybrid working also became a reality with collaboration and productivity tools.
It might have given you enough motivation to start your own SaaS business. You might have done enough research, filtered out some exciting SaaS business ideas, or even have a business plan ready.
But all of this is useless if you don’t have a SaaS business model. It is essential to ensure business continuity, and a SaaS business model will ensure your business keeps running, makes a profit, and sustains any challenge.

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
What is a SaaS Business Model?
A SaaS business model is a blueprint or a template of how a SaaS business will operate, earn revenue, and stay afloat in the market. The fundamental premise of the SaaS business model is that we host a piece of software on the cloud (which can be operated through the web browser) and charge users some fee to access it.
We face different challenges since we host a SaaS business online instead of hosting it traditionally. Hence, SaaS businesses are generally more complex and require a significant amount of design skills, coding knowledge, and an eye for the latest trends.
A SaaS business model can help you ensure you steer clear of any business challenges and can thrive in the hypercompetitive SaaS business space.
Example of a SaaS Business Model
There are many SaaS companies in the market, such as Slack, Zoom, Clickup, Trello, Netflix, etc. All these companies have different SaaS business models. They operate differently, use different approaches to charge customers (some seek one-time fees, while others work on a subscription basis), and have different revenue models.
You can also look at the different SaaS-based remote work stacks mentioned.
Types of SaaS Business Models
Different types of SaaS business models exist. Although, we can broadly categorize them into the following categories:
1. SaaS Revenue Model
A SaaS revenue model helps you understand how to profit from your SaaS business. With this model, you can define how to monetize your product and at what price. At the same time, you also understand who’s your target audience and how to market your product to them.
Here are the types of SaaS revenue models:
A. Ad-based Revenue Model
The idea is simple. First, generate significant traffic on your website or app and then sell ad space. Now, instead of charging money from people for using this product, you can sell their ad views to other companies.
There are two ways to do this:
- Directly selling page space to specific advertisers
- Use a third-party ad system like Google AdSense to find relevant ads for your area.
B. Affiliate revenue model
This SaaS revenue model is a lot similar to the ad revenue model. The only difference is that you can drive sales elsewhere by using affiliate links instead of directly earning money from people viewing your content.
It can help you earn more revenue than simply placing ads on your product. However, you risk annoying the viewers with unnecessary ads.
C. Channel Sales
In this SaaS revenue model, you don’t try selling your product/service yourself. Instead, you hire resellers who have a large audience. Various brands selling products on Amazon or other eCommerce sites are examples of this revenue model.
D. Direct Sales
As the name indicates, you directly sell your product to the consumers in this SaaS revenue model. The positive side is that you don’t have to share revenue with any reseller. However, the downside is that you’ll have to hire a sales team to achieve sales, which may cost you a fortune.
E. Freemium Model
The idea behind the freemium SaaS revenue model is to give potential customers a glimpse into your product before they decide to spare their hard-earned money on it. It is important because customers are usually reluctant to spend their hard-earned money unless they see a benefit.
F. Subscription Revenue Model
In the subscription revenue model, businesses generate revenue by charging customers some amount of fee processed at regular intervals. The video streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime follow this SaaS revenue model.
2. SaaS Pricing Model
In the SaaS pricing model, we decide on the price of your product. It is important because the pricing of a software product should be an informed decision. Also, by analyzing your competitors, you can set prices that give you a competitive advantage.
Here are some most successful SaaS pricing models that always work:
A. Flat Rate
It is the most straightforward SaaS pricing model, offering a flat price for a service on a monthly or annual fee. We provide no customization initially, but we can change the price plan to accommodate different packages as traffic starts pouring in. You can also iterate through the product to include better and newer services.

B. Per-User Pricing
This pricing model is quite popular in SaaS companies. The idea is simple, and when you charge per user, the pricing also goes up. The pricing is suitable for small and mid-sized businesses as it can be costly for large-scale enterprises, and they would go for SaaS software with one-time costs.
C. Tiered Pricing
In tiered pricing, we divide the pricing into different plans. The pricing of each plan depends on what we’re offering in it. The more features a plan provides, the more its price is.
When creating different plans, ensure that each plan suits the particular needs of your different buyer personas. Offer a free-tier or low-cost plan that suits small-scale business needs and scale-up features and pricing for large-scale enterprises.

D. Pay-as-you-go Basis
This pricing plan is popular among cloud-based providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Here, the subscriber pays only for what they use, i.e., they rent the service, use it till it is needed, and repay it for the service when they need it again. It is like paying your electricity bill, only paying for what you use.
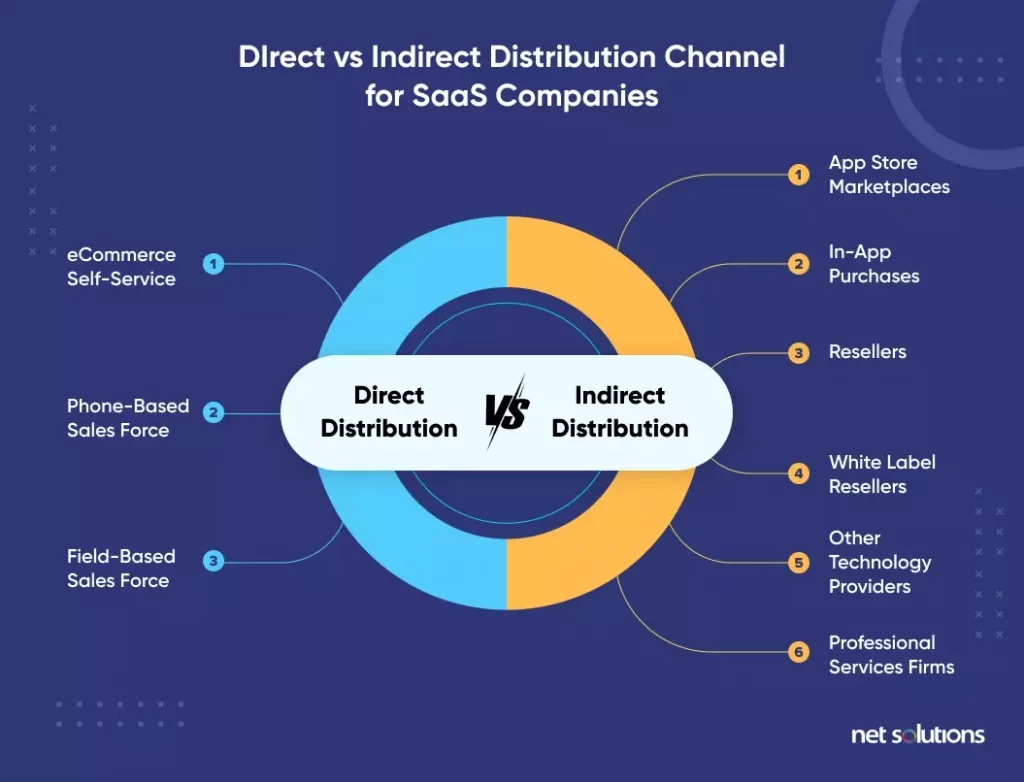
3. SaaS Distribution Model
The SaaS distribution model is about how we distribute our offerings to consumers, and we consider who sells the product to the customer and their method.
Two types of SaaS distribution models exist:
- Direct Distribution: In direct distribution, your employees, staff, and technical assets contact and sell to the customer. The company’s website and telephone-based or video conferencing sales force are among the most common channels we leverage
- Indirect Distribution: You will involve a third party to contact and sell your product or services to your customers in indirect distribution. App store marketplaces, in-app purchases, resellers, and professional services firms are some channels we use.
These SaaS distribution models will depend on your budget and what you plan to achieve.
Top 5 Compelling Benefits of the SaaS Business Model
While reading this, you may wonder why SaaS is the best business model. It is because SaaS has some compelling advantages to offer. The most prominent ones are :
1. Speed of Innovation Gives Competitive Edge
Cloud computing allows a greater innovation scope, leading to an unconventional product that can potentially disrupt the market. When your new product is built on SaaS, and you launch it quicker in the market, you can expect to upscale the SaaS product adoption rates. Where others might be still brainstorming to launch a traditional in-house software, you’ll offer value through the cloud, thus helping you stay one step ahead of the competition.
SampleBoard is an example of how SaaS can give you a competitive edge. Rosslyn Tebbutt, an interior designer at SampleBoard, wanted to create a SaaS application that could help draft visual design concepts. Net Solutions created a custom product that stood relevant to the designer industry using the agile software development method. Here is the case study.
2. Product-Market Fit = Minimum Marketing Efforts
With your SaaS product, you can reach your target audience promptly by enabling cloud access. You can solve your customers’ problems if you achieve the product-market fit.
It further leads to word-of-mouth marketing where one user recommends the product to other potential users, thus reducing your efforts in marketing and paving the way to increased SaaS sales.
3. The Anywhere, Anytime Value USP
When you offer a SaaS product, you ensure the 24x7availability of your services from anywhere and at any time. This remote, all-time access is an asset for businesses affected by COVID-19. Companies have been operating on the cloud and using cloud-based applications for collaboration, communication, and continuing with daily tasks.
If you step into the market now with the idea that addresses the target audience’s needs, you’ll successfully be able to achieve a Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
4. Faster Time to Market Means Quick Iteration Through the MVP
It can take years to build an organization’s product and even an MVP, which, in turn, takes time to validate. A SaaS-based product can solve this issue as it does not require installation, and instead, it only needs access to the World Wide Web.
This way, we can launch an MVP faster, access to the product becomes more effortless and receive feedback more quickly, which further aids in quicker iterations and better value offering.
5. Income Predictability Helps Reduce Churn Rate
You can expect a recurring revenue stream over the one-time costs associated with traditional licensing software and subscription-based services. You can easily monitor the data on your deployed CRM dashboards to give insight into your product’s performance in the market.
If the growth rate drops, you can lay plans to reduce the churn rate based on both self and competitor analysis.
Disadvantages of the SaaS Business Model
1. Longer time to conversion
Adopting a SaaS service is not a small decision for customers. Especially for expensive SaaS solutions, customers will think twice before paying. Companies have a long sales process involving sales representatives, live product demos, team orientations, etc.
2. Easy to Emulate Business Model
Competitors emerge and try to emulate your success as you grow and succeed. Unfortunately, emulating your success becomes easier in SaaS business models. Your competitors can quickly determine your marketing strategy, pricing structure, sales strategy, and email campaigns from the web. Hence, you become one of many companies selling SaaS products or services.
3. Tough Competition
Building a SaaS business is easy, but keeping it afloat is the real challenge. You must keep an eye on competitors trying to copy your success and find new ways to engage users. Even the slightest carelessness in product or marketing strategy can make you lose valuable customers.
4. SaaS Businesses are Prone to Security Threats
Like everything else on the web, a SaaS business is not immune to security threats. With so many cybercrime and data loss incidents, these cyber threats have become a key concern for SaaS business owners.
43% of organizations suffered unrecoverable data loss within the last 12 months, and 63% of organizations have suffered a data-related business disruption within the past 12 months. – International Data Corporation
5. A Large Capital is Required to Run and Scale a Business
Running and scaling a SaaS business is the biggest challenge. A lot of things matter when it comes to scaling a business idea. It would help if you had data analytics to make informed decisions. You must also have a product development team to add new features, a customer support team to ensure you’ve resolved your customers’ problems on time, and a marketing team to navigate customers through the sales funnel. All of these things will need capital. Without it, you can’t survive for long.
How Do You Implement a Successful SaaS Business Model?
Creating a SaaS solution that proves a product-market fit should be your priority and objective. (Knowing the difference between a PoC, MVP, and prototype will help you better understand the product development process.)
Here is the sequence of steps that you need to navigate to ensure the successful implementation of a SaaS business plan-
- Come up with a breakthrough idea.
- Create a proof of concept if needed. It will help validate the product idea.
- Create a prototype. It will help attract seed funding for the product.
- Create and launch an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) based on the freemium model. It will help establish a basic product version that will help record initial user reactions and feedback.
- Learn from the feedback and venture into developing a full-fledged product
- Strategize around the pricing model that suits your SaaS offering
- Market. Iterate. Grow. Repeat
6 Essential SaaS Metrics to Track for Success
To ensure your company grows at the desired rate, you must track its revenue, churn, leads, etc. For this, you need to keep in mind the essential SaaS metrics that we’re mentioning below:
1. Customer Churn Rate
Customer churn rate measures how many customers you lost in a specific period and the efficiency of your business.
While measuring churn rate, ensure you’re not just digging the numbers. Also, pay close attention to the persona of these churned customers to understand why they left and how you can retain them.
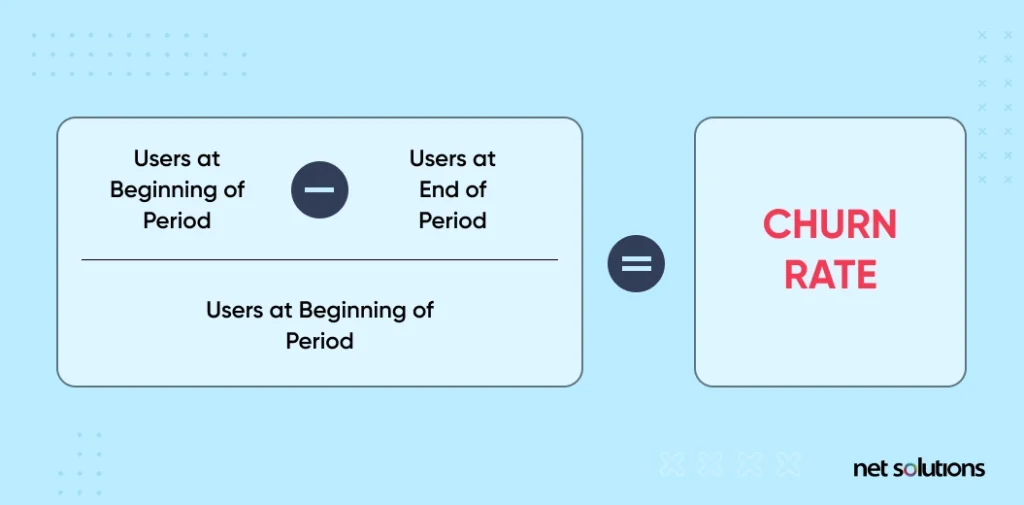
2. Revenue Churn
Revenue churn refers to how much revenue you have lost in a specific period. It is essential, especially if some customers generate more revenue than others and may have different impacts than others.
We would advise you to measure both customer churn rate and revenue churn to avoid being shocked at the massive difference in numbers.
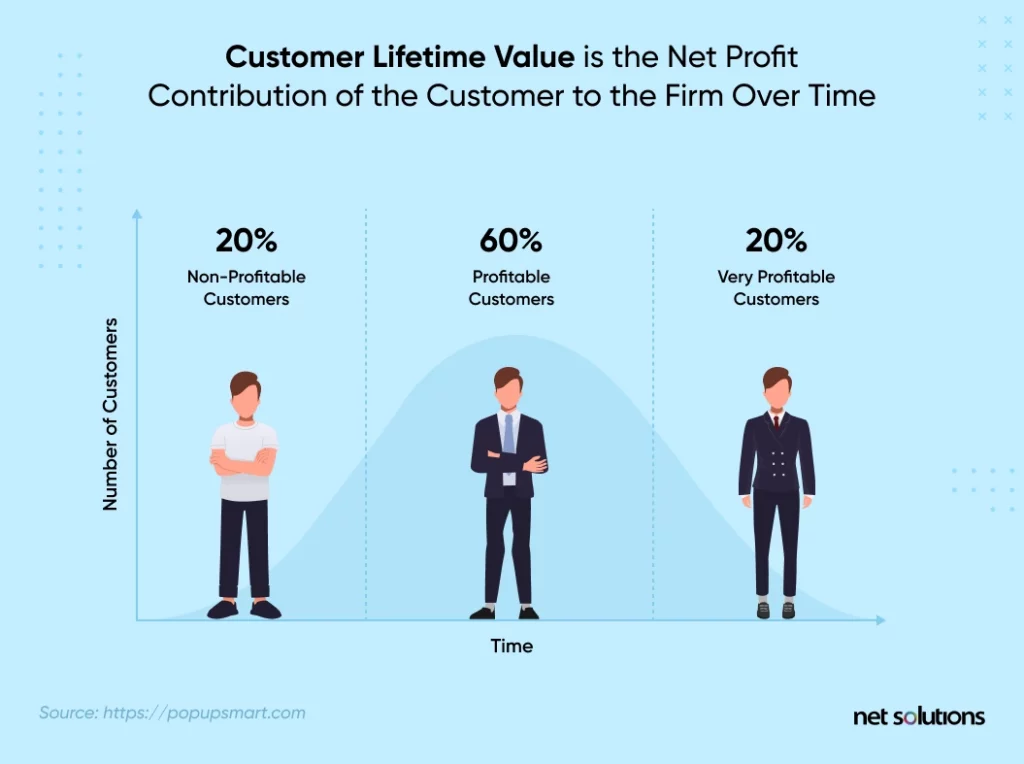
3. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer lifetime value (CLV) refers to the total revenue generated by a customer throughout the interaction with your brand. Here’s how you can calculate the customer lifetime value:
(Customer revenue x customer lifetime) – the cost of acquisition and maintenance
The longer customers use your service, the higher the customer lifetime value. This SaaS metric offers you a great perspective on how valuable a customer is to you.
4. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer acquisition cost is the amount of money a company spends on sales and marketing to acquire customers. Here’s how you can calculate this SaaS metric:
Total sales and marketing spend/ New customers added during a given time
5. Months to Recover CAC
This SaaS metric measures how many months it would take to generate enough revenue to cover the cost of acquiring a new customer. We measure it when the customer starts generating ROI for your business.
Here’s how you can calculate months to recover CAC:
Customer Acquisition Cost/Monthly recurring revenue x gross margin (gross revenue – the cost of sales)
6. Customer Engagement Score
Customer engagement score measures how engaged customers are with your product, i.e., how often they log in, how much time they spend on it, and any other indication that they will or will not churn.
Following are the inputs you can consider to track your customer engagement score:
- Product/Service Engagement: How often the client uses your product/service.
- Marketing Engagement: How often does the customer attend webinars and events about your product.
- Community Engagement: Does the client actively participate in your community?
- Advocacy Engagement: Is the client an active advocate of your product?
Frequently Asked Questions
Following are three phases of a SaaS business:
- Stage 1: Finding the right product-market for your business.
- Stage 2: Identifying a profitable, repeatable, and scalable sales model.
- Stage 3: Scaling the business based on the market demand.
It will take around 9-12 months to get your SaaS product right, and you must give another 6-12 months to achieve revenue. So, you can expect your SaaS business to be profitable after around 1.5-2 years.
- Most SaaS vendors make money via a usage-based pricing model, such as a monthly subscription.
- Some offer free services that use advertisements to earn revenue.
- A few SaaS enterprises also promote the sale of upgraded or premium versions for additional fees.
- Pay-Per-User
- Pay-Per-Active-User
- Volume Pricing
- Per-Storage Pricing
- Feature-Based Pricing
- Pay-As-You-Go
- Flat-Rate
- Free, Ad-Supported